Fig. 7.
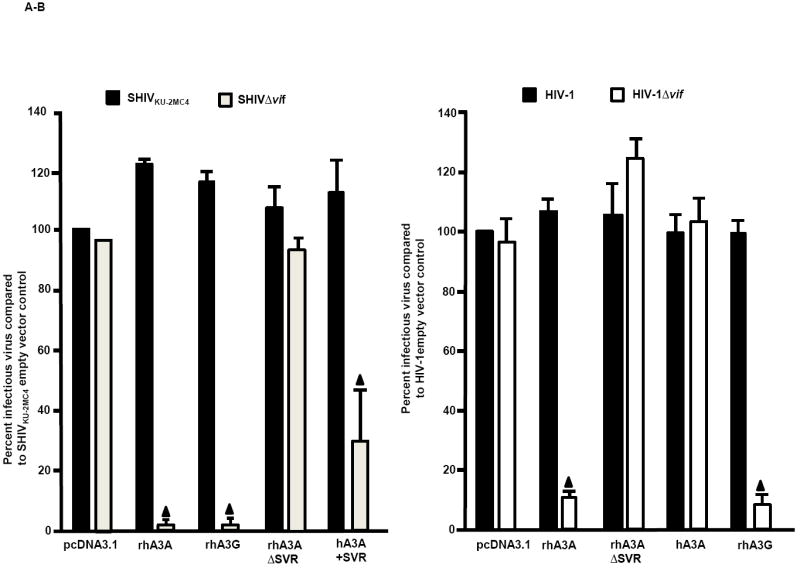
Deletion of three amino acids from the N-terminal region of rhA3A abolishes restriction. Panel A. RhA3AΔSVR is inactive against SHIVΔvif. 293 cells were co-transfected with (1.0 μg) SHIV and SHIVΔvif molecular clones with vectors expressing (0.5 μg) rhA3A, rhA3AΔSVR, rhA3C, rhA3G or empty vector (pcDNA3.1) in a 12-well plate. At 48 h, the culture medium was harvested, assessed for p27 and the amount of infectious virus titrated on the TZM.bl cells. Panel B. RhA3AΔSVR is inactive against HIV-1Δvif. 293 cells were co-transfected with (1.0 μg) HIV-1 and HIV-1Δvif molecular clones with vectors expressing (0.5 μg) rhA3A, rhA3AΔSVR, hA3A, rhA3G or empty vector (pcDNA3.1) in a 12-well plate. Virion infectivity was calculated normalizing to the wild-type HIV-1 empty vector control. In both panels A and B, the assays were run at least in triplicate. Significance in the restriction was determined with respect to the wild-type empty vector control using a two-tailed Student’s t-test (p<0.05; ▲).
