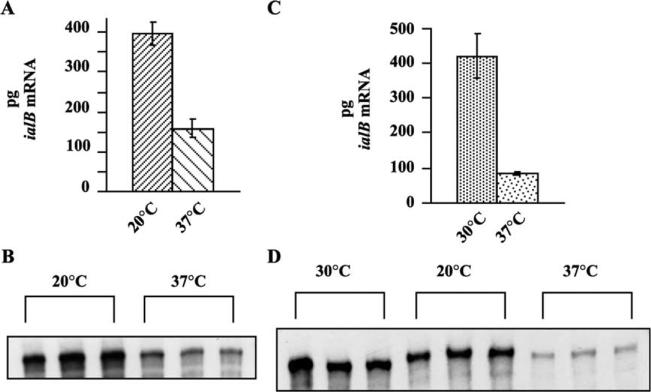
Fig. 2.
Effect of temperature shift on B. bacilliformis ialB mRNA levels. (A) In a representative experiment, the amount of ialB mRNA decreased 60% when B. bacilliformis grown at 20 °C were temperature upshifted to 37 °C. (B) NPA shows the amount of ialB mRNA decreases when bacteria grown at 20 °C (3 lanes on the left) are temperature shifted to 37 °C (3 lanes on the right). (C) Temperature upshift of 30 °C-grown B. bacilliformis to 37 °C resulted in an 80% decrease in the amount of ialB mRNA in a representative experiment. (D) No significant differences were seen between the amounts of ialB mRNA in 30 °C-grown B. bacilliformis (left 3 lanes) and bacteria temperature shifted to 20 °C (center 3 lanes); however, mRNA decreased significantly in bacteria shifted to 37 °C (right 3 lanes).