Scheme 4.
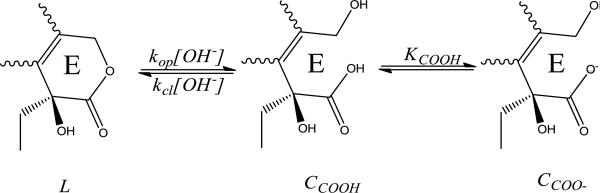
The proposed mechanism for reversible, pH dependent ring opening of TPT from its lactone, L, to carboxylate, CCOO-, form. Because ring opening proceeds through the carboxylic acid species, CCOOH, ring opening increases as more carboxylate is formed at higher pH, as governed by the acid dissociation constant for the E-ring carboxylic acid, KCOOH.
