Fig. 1.
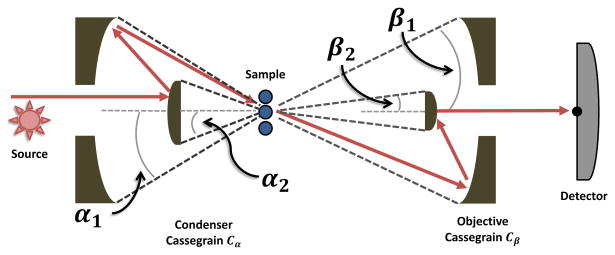
The optics in an IR imaging system consist of a mid-infrared source (modulated by an interferometer here), two Cassegrain reflectors for condensing (Cα) and collecting light (Cβ) and a detector. Each Cassegrain is characterized by the collecting angles (α1 and β1) specified by the numerical aperture (NA), and the angle subtended by the secondary (internal) mirror (α2 and β2). Note that scattering from a sample may change the angle of the propagating wave, as shown schematically here.