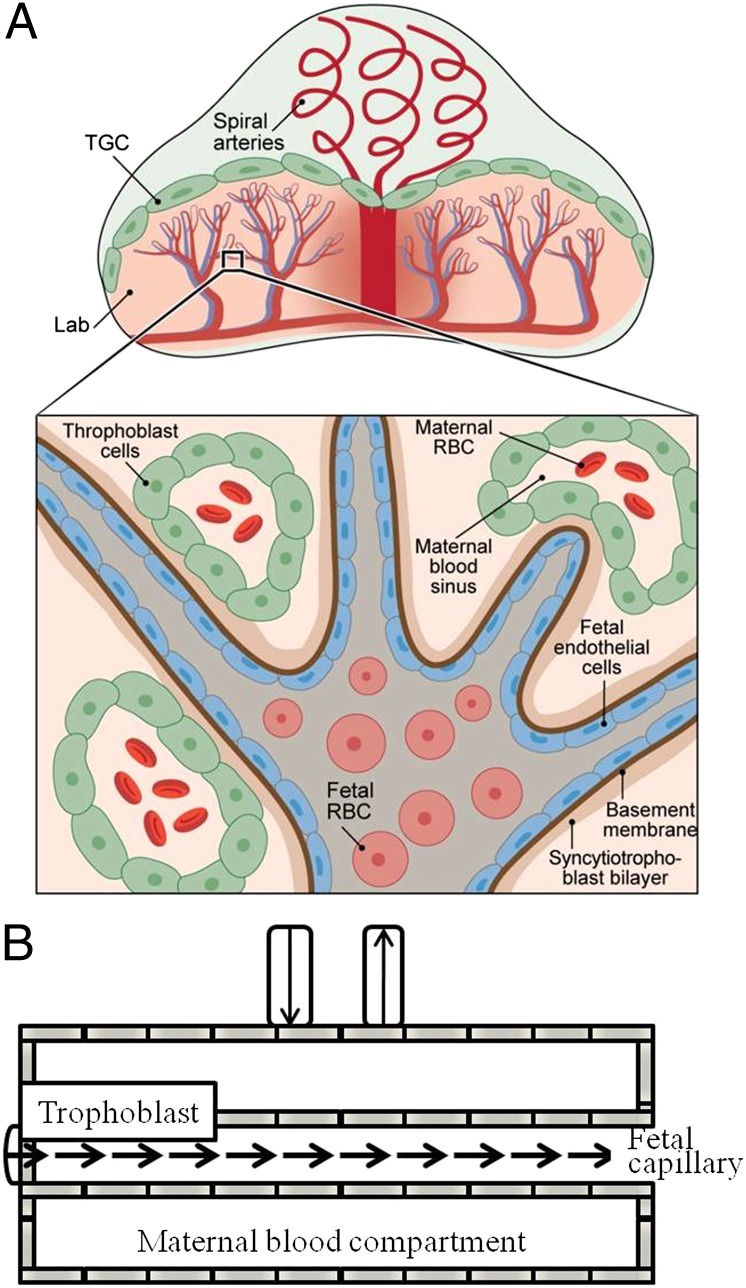
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagrams summarizing (A) the structure and main components of a mouse placenta and (B) the movement of fluids in each of these main compartments as visualized by diffusion MRI. Inset in A details the fetal–maternal–trophoblastic interactions in the labyrinth (Lab) area: Fetal cells are surrounded by endothelial cells and membranes; fetal capillaries are surrounded by maternal blood sinuses, which conduct red blood cells (RBC) and are lined by trophoblast cells. Fluid exchanges between the fetal capillaries and the maternal blood pools are mediated by the trophoblasts, including the trophoblast giant cells (TGC).