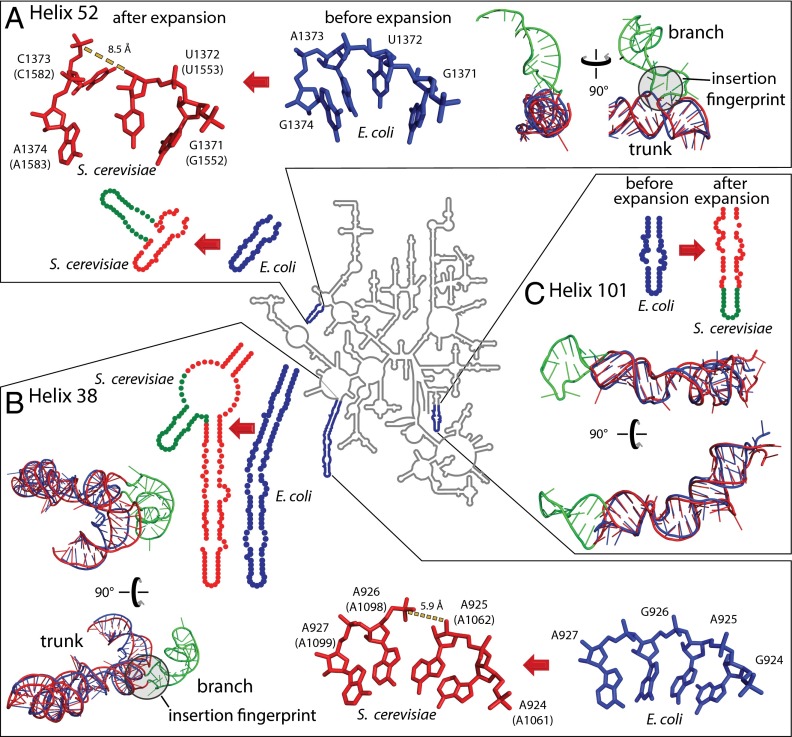
Fig. 4.
rRNA expansion elements in two and three dimensions. (A) Helix 52 is expanded by insertion. (B) Helix 38 is expanded by insertion. (C) Helix 101 is expanded by elongation. The secondary structure of the LSU common core rRNA, represented by that of E. coli (34), is a gray line at the center of the figure. Selected regions where the E. coli rRNA has been expanded to give the S. cerevisiae rRNA are enlarged. In the enlargements, the rRNA is blue for E. coli and red for S. cerevisiae, except that expansion elements of S. cerevisiae rRNA are green. These observed expansion processes, from blue rRNA to red/green rRNA, are symbolized by red arrows. Superimposed pre- and postexpanded rRNAs indicate trunk (old) and branch (new) elements. Insertion fingerprints, where trunk meets branch, are highlighted by gray circles. E. coli nucleotide numbers are provided, with S. cerevisiae numbering in parentheses.