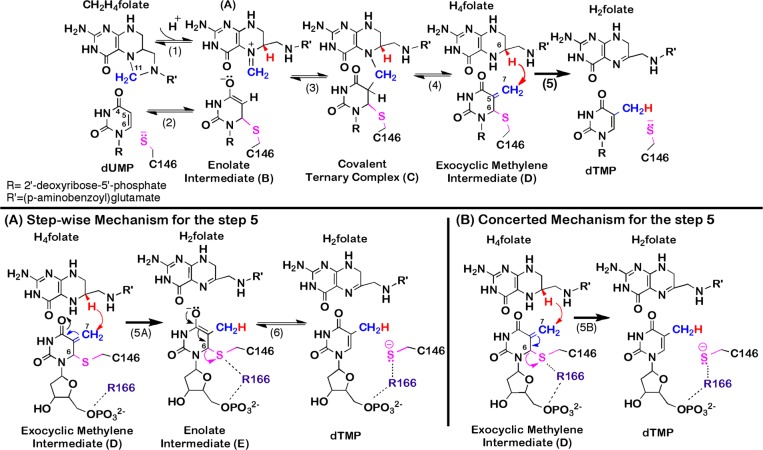
Scheme 1. Proposed Chemical Mechanism for TSase.
(Top panel) Proposed mechanism for TSase (adapted from ref (2)). The reaction is initiated by Michael addition of the enzymatic cysteine (C146) at C6 of dUMP (step 2) that leads to the formation of a covalent TSase-dUMP enolate intermediate (B), followed by Mannich condensation (step 3) to form a covalent ternary complex of TSase-dUMP-CH2H4folate (C). Following the Hoffman elimination (step 4), the methylene group forms an enzyme-bound exocyclic methylene intermediate (D). Finally, a hydride is transferred from C6 of H4folate to C7 of compound D and C146 departs from the product dTMP (step 5). (Bottom panels) Proposed mechanisms for step 5. (A). A stepwise mechanism that proceeds through the formation of a covalent TSase-dTMP enolate intermediate (compound E, similar to the compound B in the top panel).8,9 (B) A concerted mechanism where the hydride transfer takes place concomitantly with the C–S bond cleavage.5,7