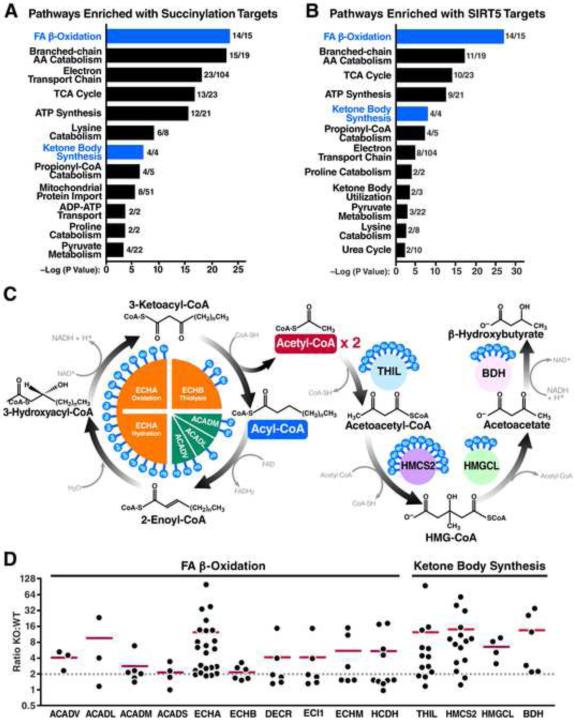
Figure 4. Fatty acid β-oxidation and ketone body synthesis are highly targeted by SIRT5.
(A, B) Pathway analysis of succinylation (A) and SIRT5 targets (B) with the number of proteins identified per pathway. Fatty acid β-oxidation and ketone body synthesis are highlighted in blue. (C) Schematic depicting the core machinery of fatty acid β-oxidation and ketone body synthesis with SIRT5 target sites indicated on each protein. (D) Succinylation profiles of enzymes involved in fatty acid β-oxidation and ketone body synthesis. KO:WT ratio of each SuK site is shown in scatter plots. Red horizontal bar represents the median KO:WT ratio of all SuK sites on each protein. Dotted line indicates a KO:WT ratio of 2.
Abbreviations include very long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (ACADV), long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (ACADL), medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (ACADM), short chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (ACADS), trifunctional enzyme α subunit (ECHA) and β subunit (ECHB), 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase (DECR), enoyl-CoA delta isomerase 1 (ECI1), short chain enoyl-CoA hydratase (ECHM), short chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (HCDH), acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase (THIL), 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A synthase 2 (HMCS2), 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutarate-CoA lyase (HMGCL), and 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (BDH).