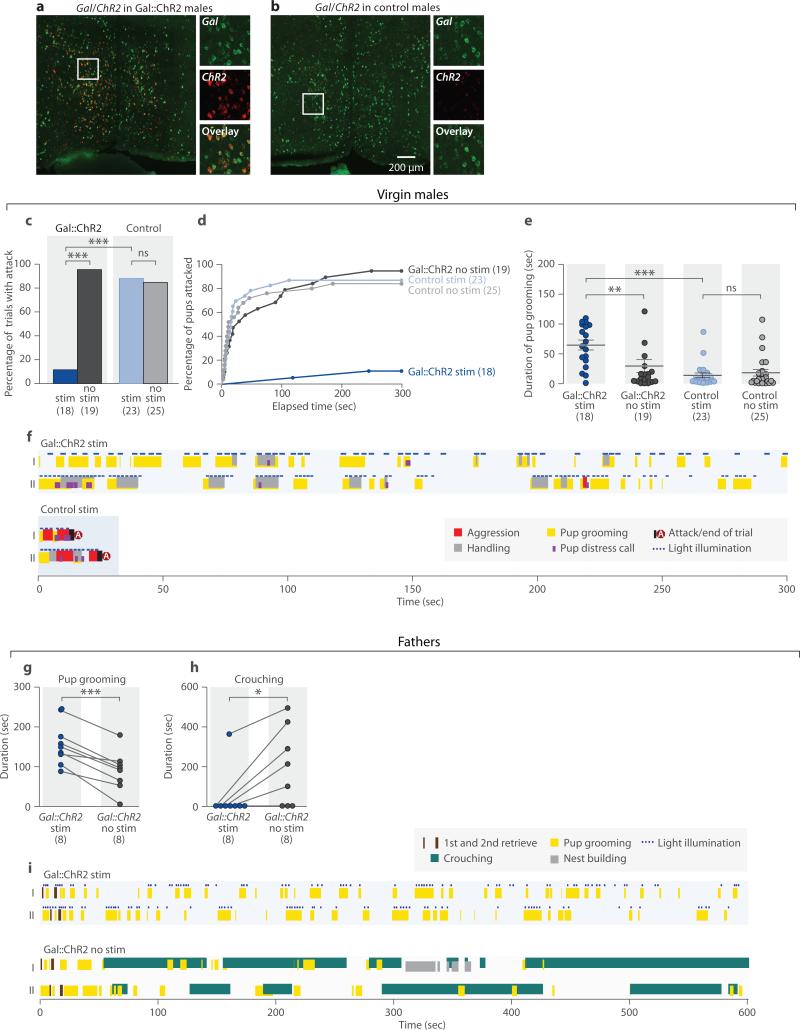
Figure 5. Optogenetic activation of MPOA Gal+ neurons in males suppresses attack and promotes pup grooming.
a-b, Co-labeling Gal and ChR2:EYFP expression in the MPOA of the Gal::ChR2 and control males. c, Percentage of trials with attacks of pups by virgin males. Fisher's exact test with Bonferroni correction, ***P<0.001, ns. not significant. d, Percentage of pups attacked by each group of virgin males. Gal::ChR2 stim trials are significantly different from Gal::ChR2 no stim and control stim trials. Kolmogorov-Smirnov test with Bonferroni correction, P<0.001. e, Pup grooming in the tests with virgin males. Mean±SEM; Mann-Whitney test with Bonferroni correction. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ns. not significant. f, Sample behavior raster plot of Gal::ChR2 stim and control stim trials in virgin males. Note that two behavior elements (such as pup grooming and handling) can occur simultaneously. g, Pup grooming in the tests of fathers. N=8 for each group, t-test pairing the same animal with and without light stimulation, ***P<0.001. h, Crouching in the tests of fathers. N=8, paired t-test, *P<0.05. i, Sample behavior raster plot of Gal::ChR2 stim and Gal::ChR2 no stim trials in tests with fathers.