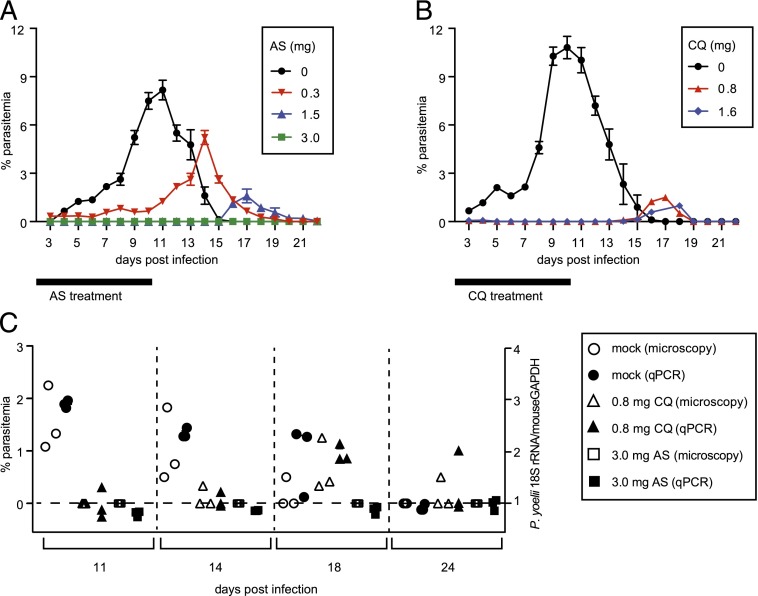
FIGURE 1.
AS-ITV can control BS parasites, whereas CQ-ITV allows the persistence of BS parasites. (A) Groups of mice infected with 10,000 wt P. yoelii spz by i.v. injection were mock treated (black circles, n = 3) or treated with either 0.3 (red inverted triangles, n = 5), 1.5 (blue triangles, n = 5), or 3.0 mg (green squares, n = 5) AS for 10 d after the infection (black bar). The y-axis shows the percentage of erythrocytes infected with parasites, as determined by microscopy of Giemsa-stained thin blood smears, and the x-axis corresponds to days p.i. (B) Groups of mice infected as described earlier were mock treated (black circles, n = 8) or treated with either 0.8 (red triangles, n = 10) or 1.6 mg (blue diamonds, n = 10) CQ for 10 d after the infection (black bar). (C) Blood samples taken on days 11, 14, 18, and 24 p.i. with P. yoelii spz as described in (A) were analyzed by thin blood smear microscopy and by qPCR quantitation of P. yoelii 18S rRNA versus the mouse GAPDH to determine the presence of parasites. The left y-axis shows percentage of erythrocytes infected with parasites as determined by microscopy of Giemsa-stained thin blood smears, the right y-axis shows the ratio of P. yoelii 18S rRNA versus mouse GAPDH detected by qPCR, and the x-axis indicates days p.i.