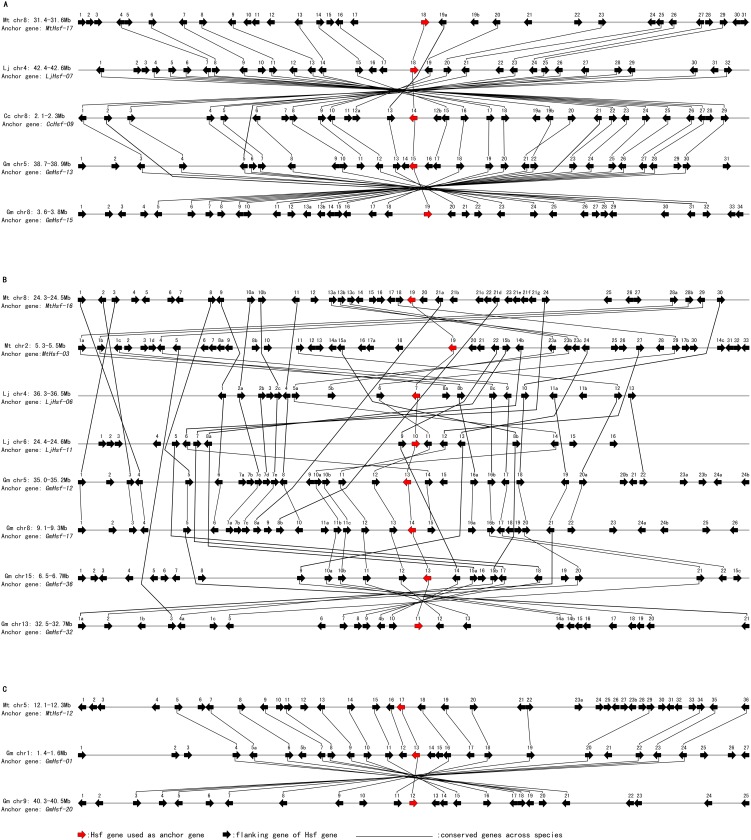
Figure 5. Comparative maps of representative Hsf genes and their flanking genes within syntenic chromosomal intervals across selected legume species.
The relative positions of all flanking protein-coding genes were defined by the anchored Hsf genes, highlighted in red. The chromosome segments are shown as gray horizontal lines, with arrows corresponding to individual genes and their transcriptional orientations. All genes are numbered from left to right, in order, for each segment. Where several duplicated genes were present within a region, these genes were given the same number, with the letters a, b, c… appended in order. Conserved gene pairs among the segments are connected with lines. (A) The syntenic chromosomal intervals containing MtHsf-17, LjHsf-07, CcHsf-09, GmHsf-13 and GmHsf-15 across M. truncatula, L. japonicus, C. cajan and G. max. (B) The syntenic chromosomal intervals containing MtHsf-03, MtHsf-16, LjHsf-06, LjHsf-11, GmHsf-12, GmHsf-17, GmHsf-32 and GmHsf-36 across M. truncatula, L. japonicus, and G. max. (C) The syntenic chromosomal intervals containing MtHsf-12, GmHsf-01 and GmHsf-20 across M. truncatula and G. max. The full microsynteny maps of the regions containing Hsf genes within M. truncatula, L. japonicus, C. cajan and G. max are shown in Figure S5.