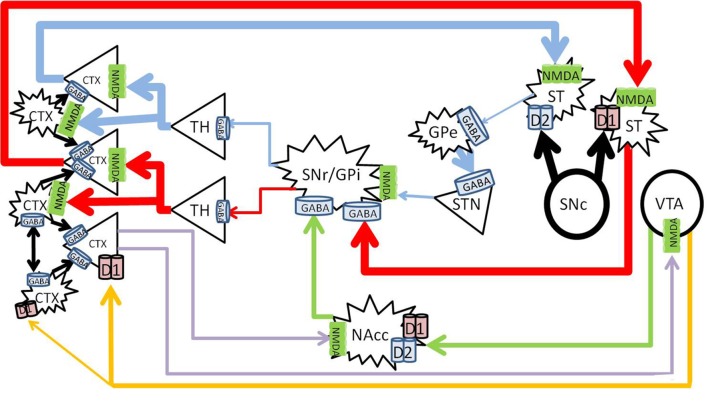
Figure 2.
Healthy effects of dopamine on dopaminergic pathways. The substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) releases dopamine into the striatum (large black arrows), and enhances thalamocortical glutamate release along the nigrostriatal pathway (blue and red). The direct pathway (red) becomes enhanced by D1 activation, and the indirect pathway (blue) becomes inhibited by D2 activation. Mesolimbic dopamine (green) to the NAc core increases GABA inhibition from the NAc core to the SNr/GPi, further increasing thalamocortical glutamate transmission. Mesocortical dopamine (orange) increases cortical pyramidal firing and simultaneously stimulates cortical interneurons, which sharpen the pyramidal signals to subcortical nuclei (blue, red, and purple). CTX, cortex; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate; GPe, globus pallidus externa; SNr, substantia nigra pars reticulata; GPi, globus pallidus interna; TH, thalamus; STN, sub thalamic nucleus; NAcc, nucleus accumbens core; VTA, ventral tegmental area. Round structures indicate dopamine cell bodies; star shaped structures indicate GABA cell bodies; triangular structures indicate glutamate cell bodies.