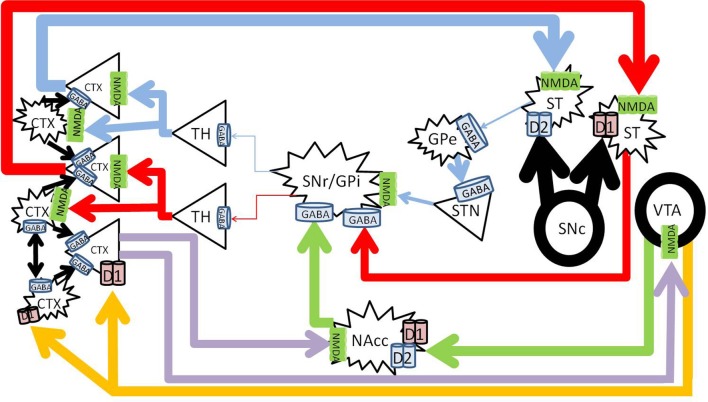
Figure 3.
Methamphetamine effects on dopaminergic pathways. Methamphetamine causes excessive amounts of dopamine to be released from the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) into the striatum (large black arrows), forcing pronounced inhibition of the SNr/GPi (red and blue). Dopamine from the VTA to the NAc increases NAc inhibition on the SNr/GPi (green). Enhanced cortical signals increases glutamate from the PFC to the NAc (purple) further increasing NAc inhibition on the SNr/GPi, and exacerbates glutamate excess in the cortex. CTX, cortex; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate; GPe, globus pallidus externa; SNr, substantia nigra pars reticulata; GPi, globus pallidus interna; TH, thalamus; STN, sub thalamic nucleus; NAcc, nucleus accumbens core; VTA, ventral tegmental area. Round structures indicate dopamine cell bodies; star shaped structures indicate GABA cell bodies; triangular structures indicate glutamate cell bodies.