FIGURE 1.
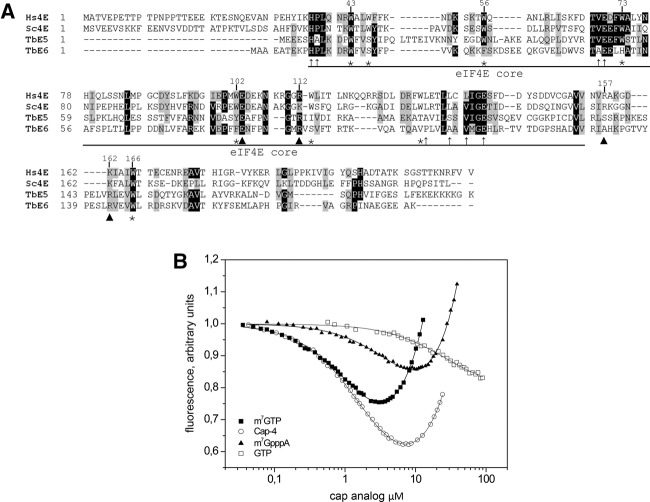
TbEIF4E5 and TbEIF4E6 are shorter than the eIF4E homologs from yeast and human. (A) Alignment of the sequences was performed using Clustal W. Identical amino acids are indicated by black shading. Amino acids defined as similar, by the BLOSUM 62 Matrix, in >60% of the sequences are shaded gray. Dashes represent spaces that were inserted to allow better alignment. Asterisks represent tryptophan residues conserved in the eIF4E protein family. Arrowheads indicate nontryptophan residues required for the interaction with the cap structure: E103 hydrogen bonded with guanine; and, basic residues at positions 112, 157, and 162 with the phosphate bridge (Marcotrigiano et al. 1997). Thin arrows indicate conserved nontryptophan residues shown to be involved in eIF4G binding (Marcotrigiano et al. 1999). GenBank Accession numbers: Hs (human) eIF4E-1, NP_001959; Sc (yeast) eIF4E, NP_014502. (B) In vitro cap-binding ability of recombinant TbE5. The fluorescence-titration curves with four cap analogs were determined by fluorescence-binding assays. The protein fluorescence was excited at 280 nm and observed at 340 nm. The WT mRNA cap in trypanosomes was represented by hypermethylated cap 4, while the typical eukaryotic cap structure was represented by both the m7GTP and m7GpppA cap 0 structures. The nonmethylated GTP served as a negative control for cap 0-specific binding.