FIGURE 1.
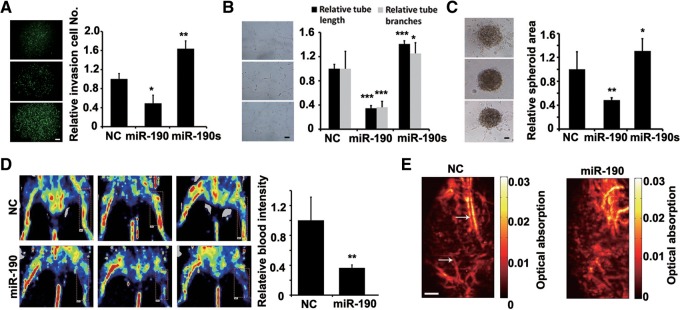
miR-190 suppresses angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. (A) Migration and invasion assays after infection of HUVECs with miR-190, miR-190 sponge, or NC vectors. NC, a scramble miRNA. N = 6. (*) P < 0.05, (**) P < 0.01 (t-test). Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Tubule formation of HUVECs infected as indicated. Representative images are shown at 12 h after plating. Quantitation of tubule branching and length. N = 5. (*) P < 0.05, (***) P < 0.005 (t-test). Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) Spheroid-based angiogenesis assay of HUVECs infected as indicated. Quantitation of cumulative length of the sprouts. N = 10. (*) P < 0.05, (**) P < 0.01 (t-test). Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Mouse hind limb ischemia model assay. Mice were injected with miR-190 or NC duplex four times after surgery (right leg). Quantitation of laser Doppler-derived blood flow in the 14th day after surgery. Three representative experiments are shown. N = 6. (**) P < 0.01 (t-test). (E) Photoacoustic microscopy imaging results of ischemic limbs treated with NC or miR-190 in the 14th day after surgery. Scale bar, 1 mm. Arrows indicate new vessels.
