Figure 3.
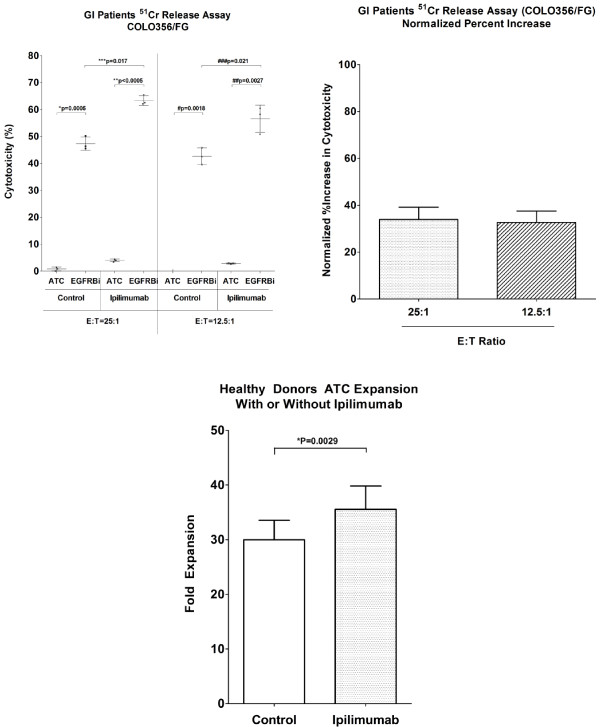
Ipilimumab enhanced BiAb-mediated cytotoxicity of ATC derived from patients with gastrointestinal cancer. T cells in cryopreserved PBMC of 3 patients with gastrointestinal cancer were expanded with 0 (control) or 50 μg/mL ipilimumab, and ATC were harvested on day 14, armed with EGFRBi, and tested for the tumor specific cytotoxicity (n = 3). (left): EGFRBi armed ATC and COLO356/FG were co-cultured at E:T ratios of 25:1 and 12.5:1 E:T ratios. For each group, a paired two-tailed t test was performed. (right): Cytotoxicity of EGFRBi armed ATC in the ipilimumab group was normalized to the control group to calculate the percent increase. Each bar represents a mean ± SE is shown for 3 patients. For each set of data, paired, two-tailed t test was performed. (lower): T cells in PBMC derived from healthy donors were activated with anti-CD3 stimulation and expanded with IL-2 in the presence of 0 (control) or 50 μg/mL ipilimumab (n = 18). Cell counts were performed at each feeding to determine the T cell proliferation. The bars represent means for each data set (paired two-tailed t test).
