Figure 1.
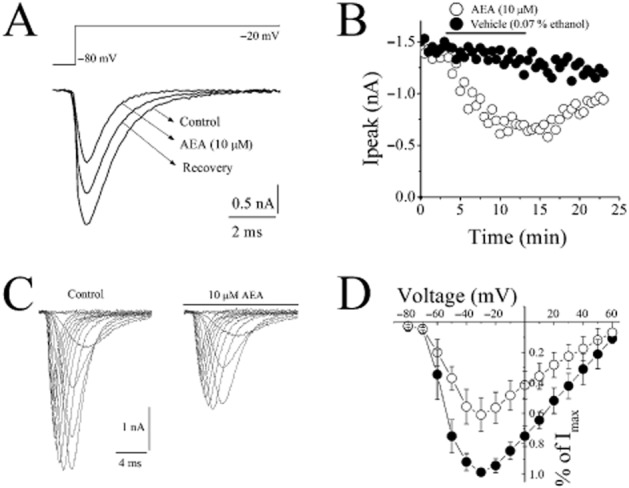
Effect of AEA on voltage-dependent Na+ currents (INa) in rat ventricular myocytes. (A) AEA inhibits INa recorded using whole-cell voltage-clamp mode of the patch-clamp technique. INa was recorded during 50 ms voltage pulses to −20 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV. Current traces were recorded before (control) and after 10 min application of 10 μM AEA. (B) Maximal currents of VGSCs presented as a function of time in the presence of vehicle (0.07% ethanol) and 10 μM AEA (n = 5–6 cells). (C) Representative recordings of INa in response to pulse protocol shown, under control conditions and after application of 10 μM AEA. (D) Normalized and averaged I–V relationships of control INa and INa in the presence of 10 μM AEA, determined by applying a series of step depolarizing pulses from −80 to +70 mV in 10 mV increments for a duration of 50 ms. Data shown are means ± SEM); n = 5–7 cells.
