Figure 1.
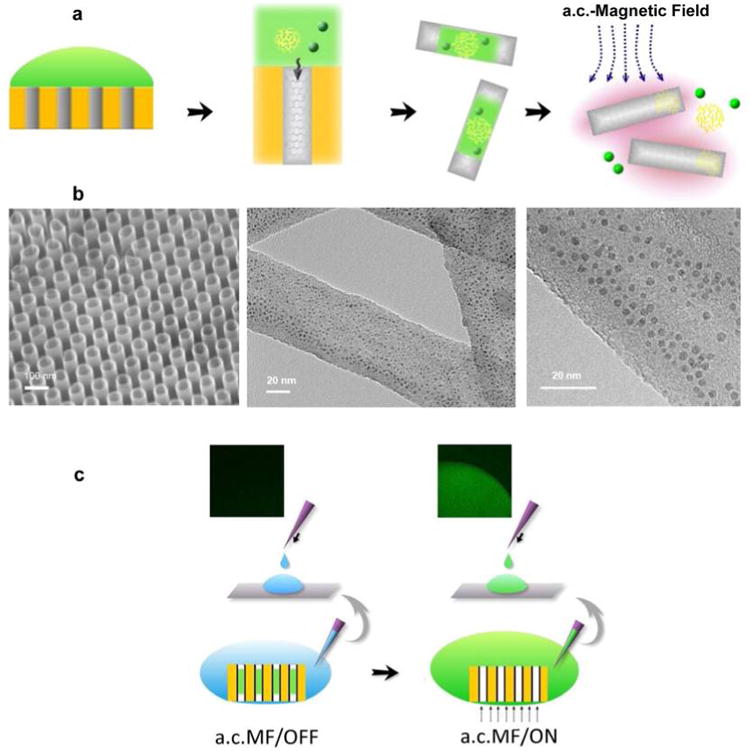
Loading and on-command release of Trojan-Horse nanotubes by the induction heating of CNTs. (a) Schematic illustration of filling QDs/gelatin/drug into nanotubes. The payload is loaded into the nanotubes array by the vacuum suction at the back side of the template followed by the release of Trojan-Horse nanotube from template by chemical dissolution of AAO template. Finally, the payload is released from the Trojan-Horse nanotubes by exposing Trojan-Horse nanotubes to the a.c. magnetic field. (b, left) SEM image of highly ordered carbon nanotube array. (center) TEM image showing the high loading yield of QDs into nanotubes. (right) A magnified TEM micrograph showing the QDs with diameter ∼4 nm are inside the nanotubes. (c) QD loaded nanotube array immersed in water and subjected to an a.c. magnetic field for 30 min. Thereafter, the solution was placed onto a glass slide and visualized by epifluorescence microscopy. (left) In the absence of the a.c. magnetic field induction, luminescence was not observed. (right) a.c. magnetic field induction results in a significant green luminescent signal corresponding to the QD luminescence emission wavelength.
