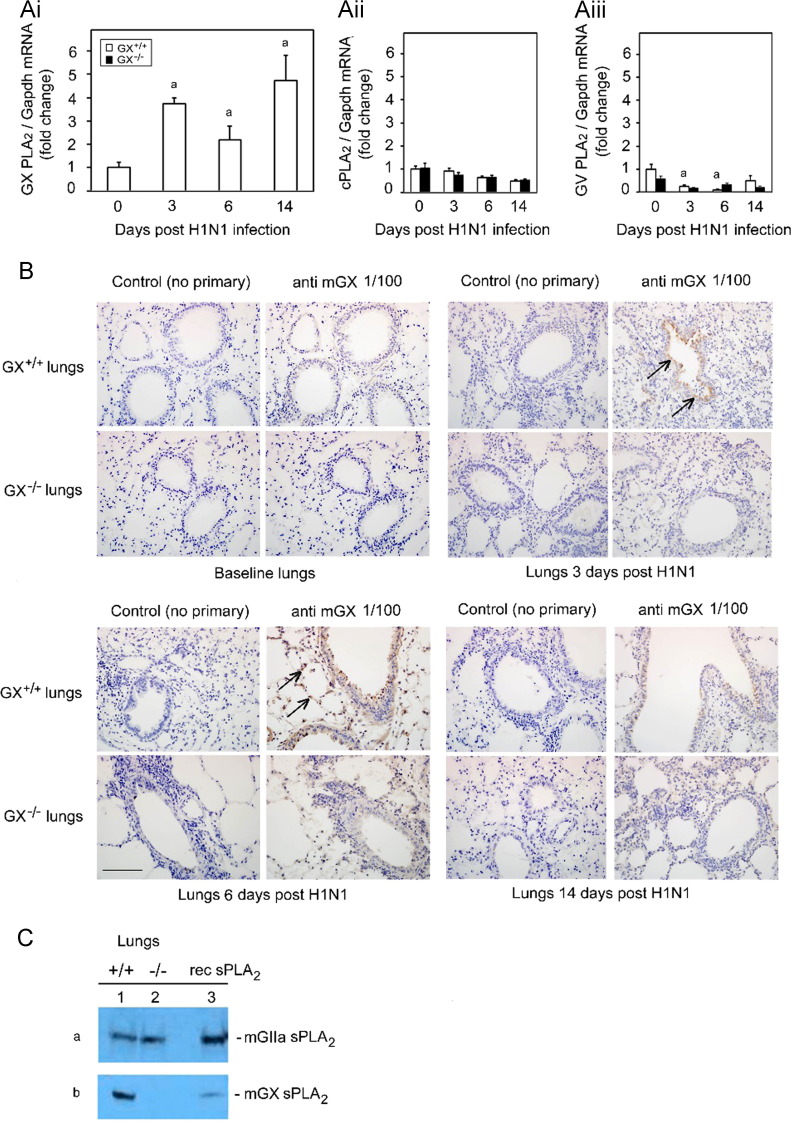
Fig. 1.
Infection with H1N1pdm influenza stimulates the expression of GX-sPLA2 in bronchial epithelial cells and inflammatory cells. Mice were infected with H1N1pdm (A/Mexico/4108/2009) and the lungs were assessed for the mRNA and protein expression and localization of PLAs during a 14 day time course. GX-sPLA2 mRNA (Ai), cPLA2 mRNA (Aii) and GV-sPLA2 mRNA (Aiii) expression quantified by Real-Time RT-PCR was normalized to GAPDH, GX+/+ (open bars) and GX−/− (filled bars) mice (C3H/HeN background mice). GX+/+ and GX−/− mouse lungs were perfusion fixed in situ with 4% paraformaldehyde, sectioned and subject to immunohistochemical analysis with the IgG fraction of rabbit anti-mouse GX-sPLA2 antiserum (1/100 dilution) (B). GIIA and GX-sPLA2 protein expression determined by immunoblot analysis of lung tissue homogenates of wild type GX+/+ (lane 1) and knockout GX−/− (lane 2) mice (C). For each blot, the corresponding recombinant sPLA2 enzyme (rec sPLA2) was run alone (lane 3) as a control. Representative results for five separate experiments are shown. All the mice used in these experiments were genotyped littermates and grouped and analyzed by their genotype. a, p<0.05 GX+/+ or GX−/− vs. base; b, p<0.05 GX+/+ vs. GX−/− at any time point, ANOVA followed by paired t-test, two tailed, assuming unequal variance. n≥8 per group; 400×; scale bar: 50 μm for immunohistochemistry.