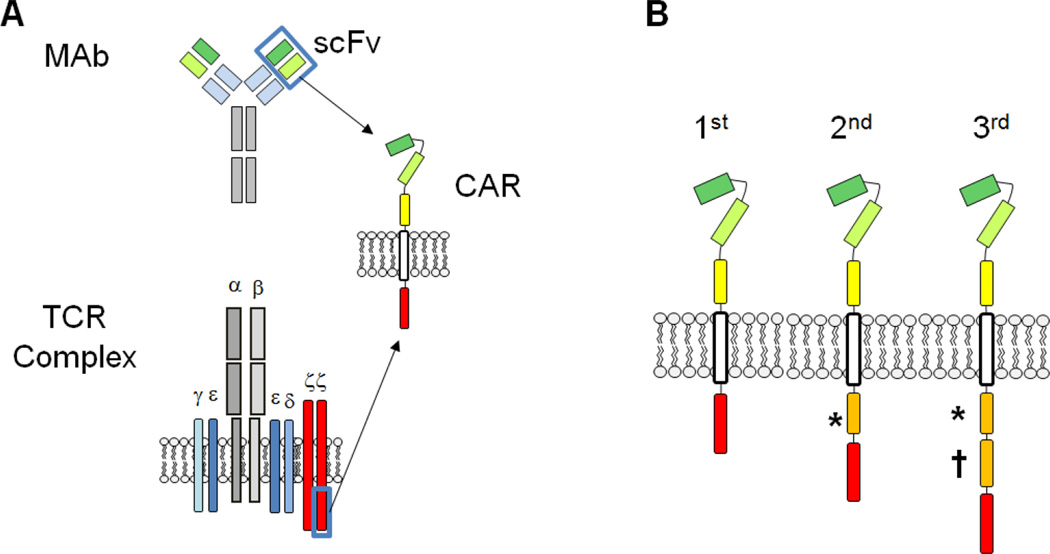
Figure 1.
Structure and design of chimeric antigen receptors (CARs). A) The extracellular, antigen binding domain of a CAR is typically derived from the single chain variable fragment (scFv) of a monoclonal antibody (MAb). The scFv segment is further linked to a transmembrane domain and an endodomain -- most commonly the signaling moiety of the T cell receptor (TCR) zeta chain. B) CARs are classified into 1st, 2nd, or 3rd generation products depending on the number of costimulatory endodomains (*, †) added to the construct. The most commonly used costimulatory endodomains in clinical and preclinical studies are CD27*, CD28*, inducible T-cell costimulator (ICOS)*, 4-1BB†, and OX40†.