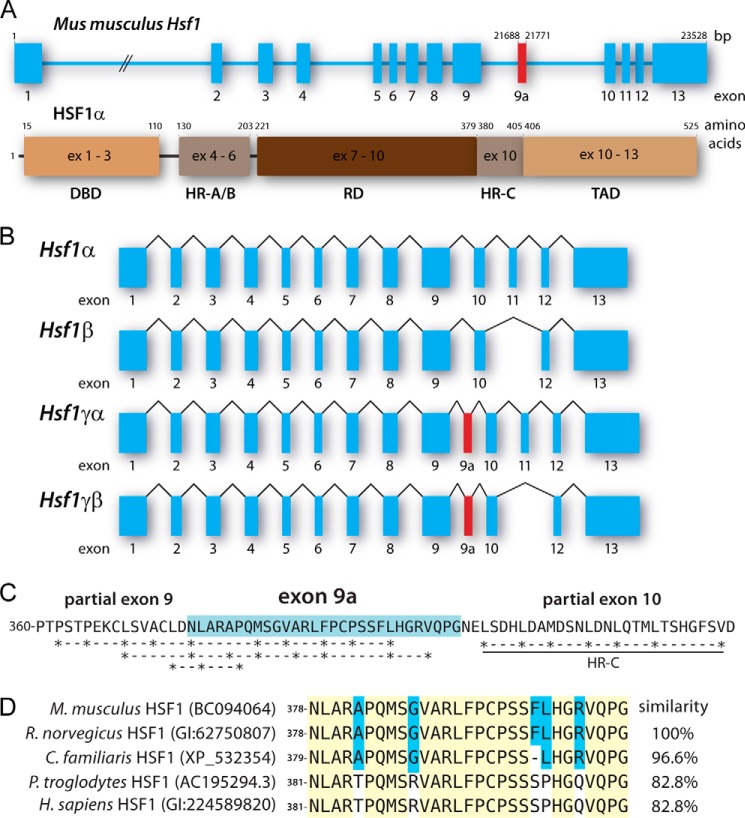
FIGURE 1.
A, schematic of murine Hsf1 gene and HSF1α protein structure (NCBI accession 15499). Exon (ex) 9a, highlighted in red, encodes the Hsf1 γ (HSF1γ) isoforms and is a 84-bp exon. The DNA binding domain (DBD) is encoded by exons 1–3, heptad repeats A and B (HR-A/B) are encoded by exons 4–6, the regulatory domain (RD) is encoded by exons 7–9 and the first two amino acids of exon 10, the heptad repeat C (HR-C) is encoded by exon 10, and the transcription activation domain (TAD) is encoded by the last seven amino acids of exons 10 and exons 11–13. B, the mRNA structures of all four possible Hsf1 isoforms. Exons are shown as boxes, and introns are shown as lines. Exon 11 defines the α and β isoforms, and exon 9a defines the γ isoforms. C, possible hydrophobic heptad repeats encoded by exon 9 and 9a. The additional amino acid sequence of the γ isoforms is highlighted in blue. D, the exon 9a encoded amino acid sequence is conserved in higher eukaryotes. The NCBI protein accession number is given in brackets after the species name. Amino acids highlighted in yellow are fully conserved; blue background depicts partial conservation. Murine exon 9a was used as reference, and the similarity of the other sequences was calculated accordingly. Genus abbreviations: M. musculus, Mus musculus; R. norvegicus, Rattus norvegicus; C. familiaris, Canis lupus familiaris; P. troglodytes, Pan troglodytes; H. sapiens, Homo sapiens.