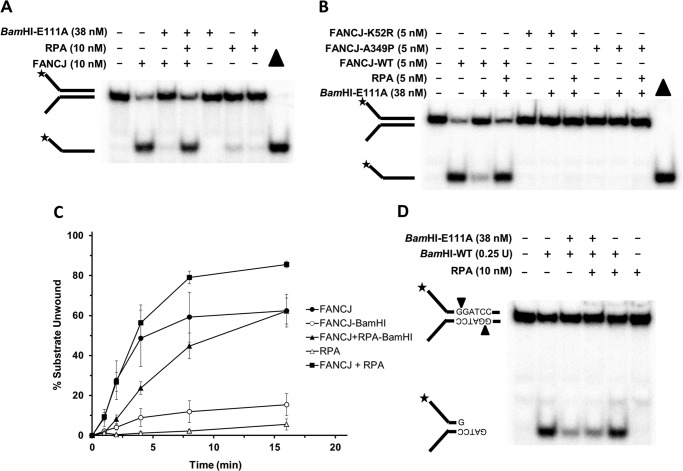
FIGURE 2.
RPA stimulates FANCJ to efficiently displace BamHI-E111A from the DNA substrate and unwind it. A, reaction mixtures containing the radiolabeled DNA substrate (0.5 nm) and the indicated proteins were incubated for 15 min at 30 °C, followed by electrophoresis of proteinase K-digested products on 12% polyacrylamide native gels. See “Experimental Procedures” for details. B, reactions mixtures were as described above except the additional presence of a Walker A box ATPase mutant FANCJ-K52R or a patient-derived Fe-S cluster domain mutant FANCJ-A349P as indicated. C, kinetics of FANCJ helicase activity in the presence or absence of RPA on forked duplex substrate pre-bound by BamHI-E111A or not. Proteinase K-digested reaction products were resolved by electrophoresis on nondenaturing 12% polyacrylamide gels. Representative gel images from at least three independent experiments are shown. D, restriction protection analysis suggests RPA does not displace BamHI-E111A bound to DNA substrate. BamHI-E111A was preincubated with DNA substrate for 15 min followed by incubation with RPA for 15 min, subsequent digestion with BamHI-WT, and analysis on nondenaturing 12% polyacrylamide gel as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The BamHI-WT cleavage product is indicated. Star denotes 5′-32P end label.