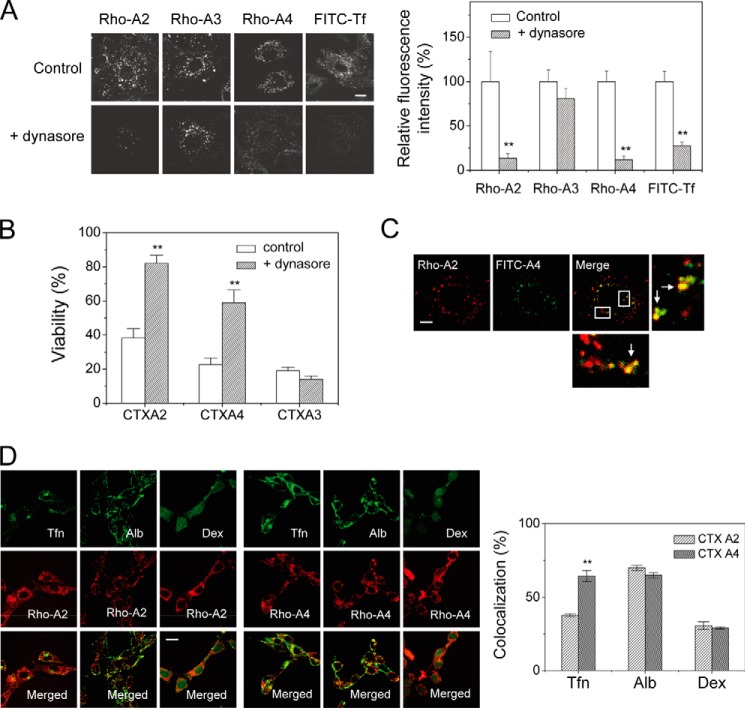
FIGURE 5.
Dynasore effect on the internalization of CTX homologues. A, CTX A2 and A4 showed dynamin-dependent endocytosis as evidenced by dynasore treatment, whereas CTX A3 endocytosis was dynamin-independent. Bar = 20 μm. B, CTX-induced cytotoxicities were performed in the absence and presence of dynasore, a specific blocker of dynamin-dependent endocytosis. Dynasore inhibited CTX A2/A4-induced cytotoxicity but had no effect on that of CTX A3. Data were mean ± S.E. (n = 5); **, p < 0.01. C, confocal images show partial colocalization of rhodamine-labeled CTX A2 and fluorescin-labeled CTX A4 in H9C2 cells. The percentage of colocalization was calculated as 67.0% (n = 5). Bar = 20 μm. D, colocalization experiments show possible endocytotic mechanisms of CTX A2 and A4. Fluorescence-labeled albumin (Alb), transferrin (Tfn), and dextran (Dex) were indicators for caveolae-mediated, clathrin-mediated, and marcopinocytosis pathways, respectively. The percentage of colocalization with transferrin, albumin, and dextran distinguished possible mechanisms of endocytosis (n ≦ 5). Bar = 20 μm. Data were mean ± S.E. (n = 5); **, p < 0.01.