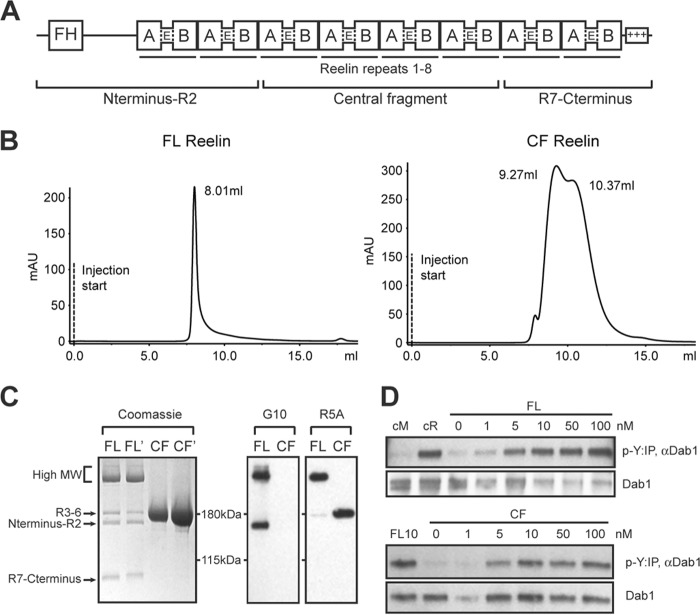
FIGURE 1.
Purification and analysis of full-length Reelin and its central fragment. A, domain structure of Reelin. Reelin contains an F-spondin homology (FH) region at N terminus, 8 repeats, and a positively charged C terminus. Each repeat contains subdomains A and B, separated by an epidermal growth factor (E)-like motif. Full-length Reelin is cleaved into three fragments. B, Full-length Reelin (FL) and central fragment (CF) proteins secreted in the culture medium of HEK293 GnTI- cells were separated by size exclusion chromatography using Superdex 200 10/300GL. FL Reelin eluted as a single peak with a MW >650 kDa, whereas CF Reelin exhibited two peaks compatible with the formation of a dimer (∼320 kDa) and a tetramer (∼620 kDa). C, Coomassie staining and Western blot analysis of purified proteins separated by SDS-PAGE. Two different batches of FL and CF Reelin were analyzed by Coomassie staining. FL Reelin contained a major band of high MW (∼350–400 kDa), and cleaved fragments of the expected size. Purified CF appeared as a single band of ∼190 kDa, corresponding to the central fragment. Western blot analysis of purified proteins with the N-terminal antibody G10 detects high MW and the N-terminal fragment of FL Reelin. The R5A antibody directed against the central fragment detects high MW and the central fragment of FL Reelin, as well as CF Reelin. D, primary cortical neurons were treated with purified FL and CF Reelin at the indicated concentrations and subjected to the Dab1 phosphorylation assay. Reelin conditioned medium (cR) and mock medium (cM) were used as controls. Both Fl and CF proteins induced robust Dab1 phosphorylation (p-Y).