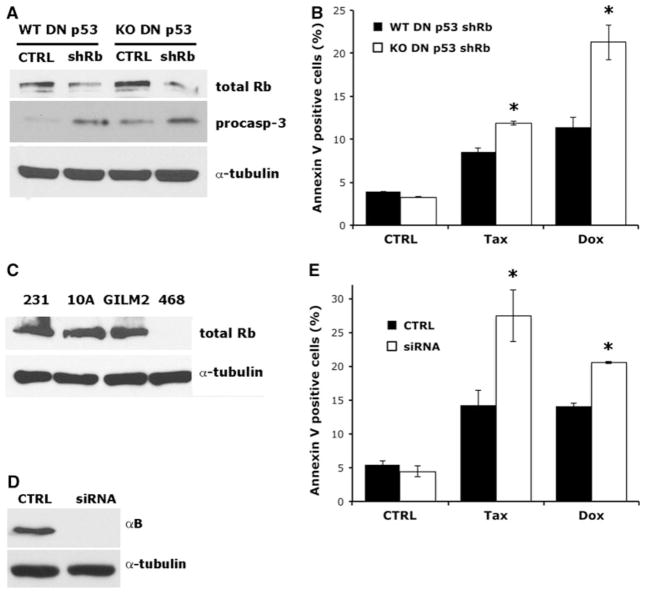
Fig. 5.
αB-Crystallin inhibits the apoptosis-sensitizing effects of Rb loss. a Immunoblot analysis of immortalized WT and αB-crystallin−/− KO DN p53 MEFs retrovirally transduced with a shRNA targeting murine Rb (shRb) or a non-silencing shRNA (CTRL). b WT and αB-crystallin−/− KO DN p53 MEFs transduced with shRb or non-silencing control were treated with vehicle, 250 nm Taxol or 1 μM Doxorubicin for 24 h. The percentage of Annexin V-positive cells was scored by flow cytometry (mean ± SD, n = 3). c Immunoblot analysis of Rb in MDA-MB-231, GILM2, and MDA-MB-468 triple-negative breast cancer cells and MCF-10A breast epithelial cells. d MDA-MB-468 triple-negative breast cancer cells were transfected with non-silencing siRNA (CTRL) or siRNA pool targeting human αB-crystallin. αB-crystallin levels were determined by immunoblot-ting. e MDA-MB-468 triple-negative breast cancer cells transfected with αB-crystallin siRNA pool or non-silencing control were treated with vehicle, 500 nm Taxol, or 3.4 μM Doxorubicin for 24 h. The percentage of Annexin V-positive cells was scored by flow cytometry (mean ± SD, n = 3). In b and e *P < 0.05 versus control WT E1A DN p53 MEFs