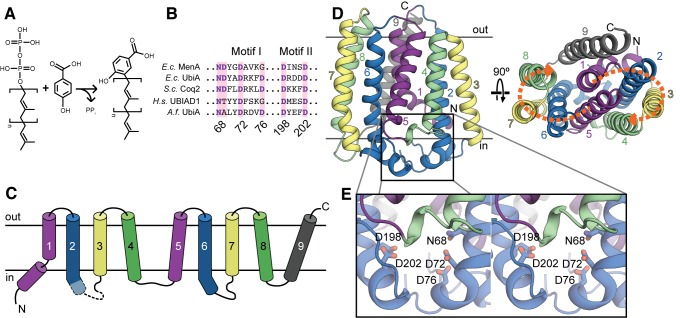
Figure 1. The UbiA fold.
(A) A representative reaction catalyzed by UbiA family members. Polyprenyl is transferred from diphosphate to 4HB to form 3-polyprenyl-4-hydroxybenzoate, a precursor to ubiquinone. The square brackets denote a single five-carbon prenyl unit. (B) The two conserved aspartate-rich motifs characteristic of the UbiA family. Residue numbers correspond to the Archaeoglobus fulgidus UbiA sequence. Ec, Escherichia coli; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Hs, Homo sapiens; Af, Archaeoglobus fulgidus. (C) Topology diagram of AfUbiA, with the transmembrane helices colored in pairs of equivalent helices in the four-helix bundles. Dashed lines indicate the region of L2–3 that is disordered in the SeMet crystal structure. (D) Cartoon representation of the AfUbiA structure viewed from within the plane of the membrane (left) and from the extracellular side of the membrane (right). The transmembrane helices are colored according to the same scheme as in panel (C). Orange arrows indicate the two pseudosymmetric bundles. (E) Magnified stereo view of the boxed area in panel (D), showing residues from aspartate-rich Motif I and II as sticks.