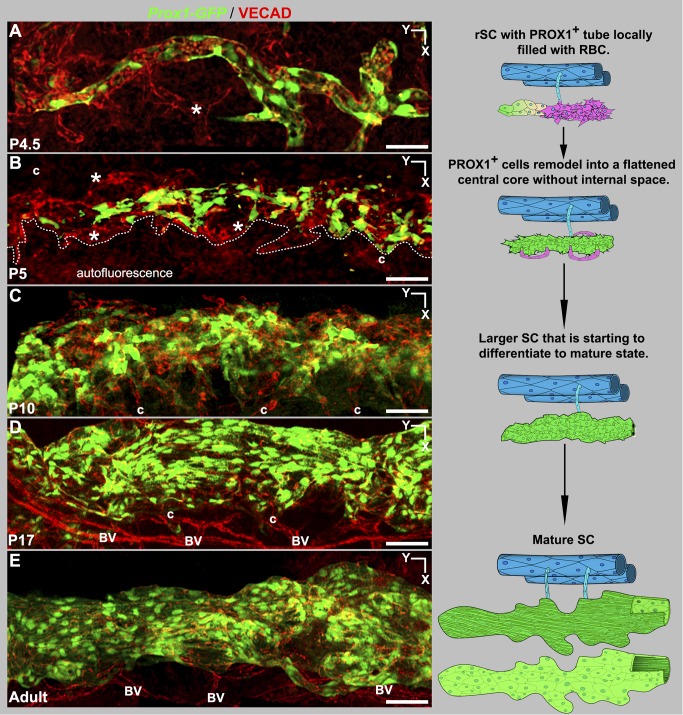
Figure 13. Development from rSC to mature morphology.
(Left, A–E) Z-projections of confocal stacks encompassing the developing SC in Prox1-GFP eyes. (A) At P4.5 VECAD labeling shows multicellular sprouts (*) at the sides of the GFP + tubular rSC. These sprouts have no detectable Prox1 expression. (B) By P5, remodeling has formed a central core of PROX1+ flattened cells without any discernible internal space or RBCs. Further development continues by sprouting (*, Figure S13) from the central core. Dotted line delineates developing SC from autofluorescence arising from nearby tissue. (C) At P10, developing SC has expanded considerably in size, and maturation with lumen formation and polarization of PROX1 expression to the inner wall have begun (see Figure 15). The developing SC remains connected to the LVP (c) but no connections to the RV are detected after P5. (D) SC looks mature at P17 but continues to grow. (E) Adult SC. (Right) The cartoons distill the essential points of each stage. At P5 PROX1- sprouts are shown in magenta. At all developmental stages, the SC is connected to the LVP. The adult stage SC cartoon attached to the LVP is seen from the inner wall perspective, where the thin cells are a darker green to depict strong Prox1 expression. The SC shown below is from the outer wall perspective, with the paler green large cells having weak or no detectable PROX1 expression. BV, blood vessels; c, collector channels. Scale bar, 50 µm.