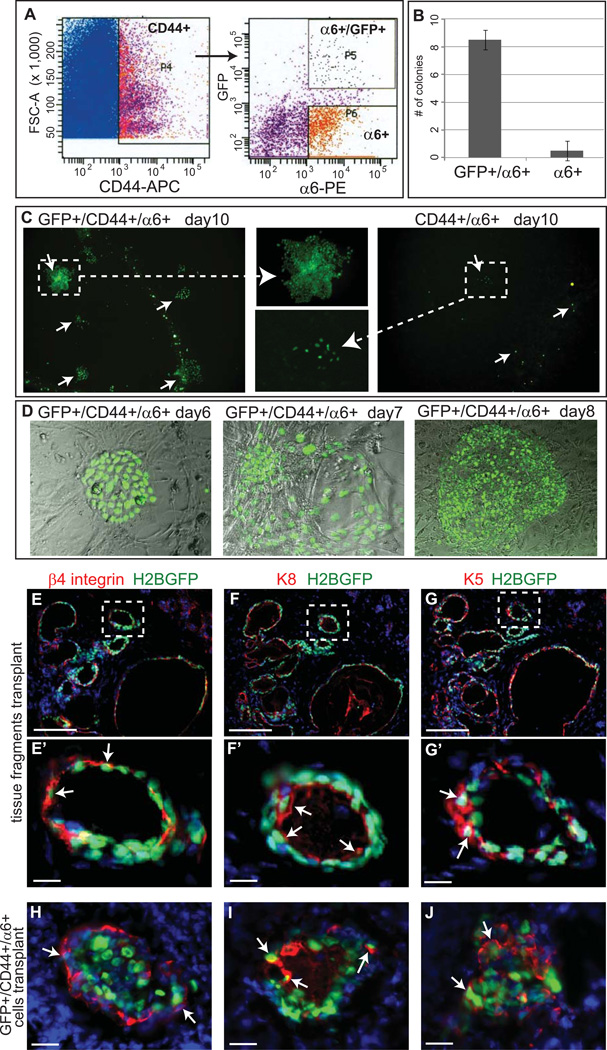
Figure 2. LRC are clonogenic and have regenerative potential.
Minor salivary glands obtained from pTreH2BGFP/K5tTA mice, 4 weeks after chase were digested and used to sort for LRCs. Epithelial marker CD44, basement membrane marker integrin α6 were used to isolate slow cycling GFP+ CD44+ α6+ LRC population and CD44+ α6+ progenitor population (A). The FACS sorted cells (LRC and progenitors) were placed in culture for clonogenic potential assessment. Colonies were counted at day 10 post sort in two independent experiments (B). The epithelial morphology of the colonies that formed from LRC and progenitors are shown (C, D). Epifluorescence of H2BGFP (green) and indirect immunofluorescence with antibodies as indicated of sections of ductal structures that formed after transplantation of dissected minor salivary glands from soft palate (E–G’) and sorted GFP+ α6+ LRC (H–J) are shown. Scale bar: E–G 100µm; E’–J 20µm. Arrows denote GFP positive cells that formed ductal like structures after transplantation.