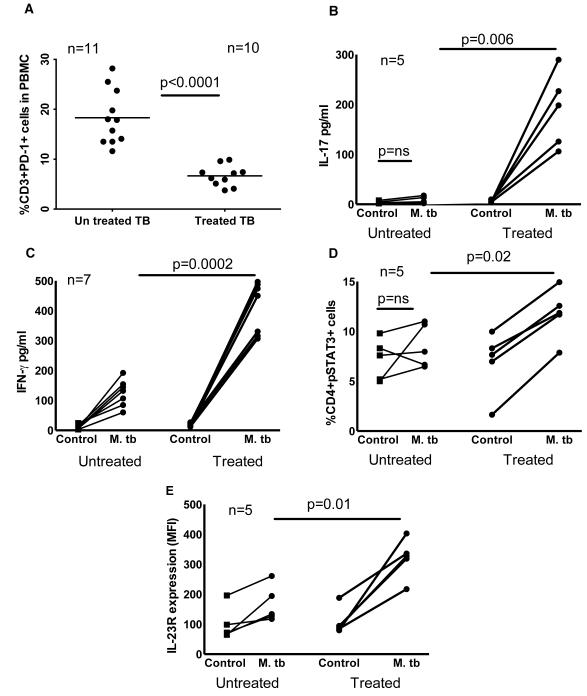
Figure 7. Effect of anti-tuberculosis therapy on IL-17 and IFN-γ production, PD-1, pSTAT3, and IL-23R expression by tuberculosis patients.
A. PD-1 expression by freshly isolated CD3+ cells. Freshly isolated PBMC from 11 untreated tuberculosis patients and 10 treated tuberculosis patients (2 years after anti-tuberculosis therapy) were stained for CD3+ and PD-1+ cells. Ten independent experiments were performed. CD4+ cells and CD14+ cells from PBMC of 5 untreated tuberculosis patients and 5 treated tuberculosis patients (2 years after anti-tuberculosis therapy) were cultured in the presence or absence of γ-irradiated M. tb H37Rv for 96 h. B. IL-17 levels in culture supernatants were measured by ELISA. Five independent experiments were performed. C. IFN-γ levels in culture supernatants were measured by ELISA. Seven independent experiments were performed. D. pSTAT3 expression by CD4+ of the above cultured cells was determined by flow cytometry. Five independent experiments were performed. E. IL-23R expression by CD4+ of the above cultured cells was determined by flow cytometry. Five independent experiments were performed. Paired and unpaired t tests were performed. Mean values for panel A, p values and number of donors (n) in each panel are shown.