Figure 1.
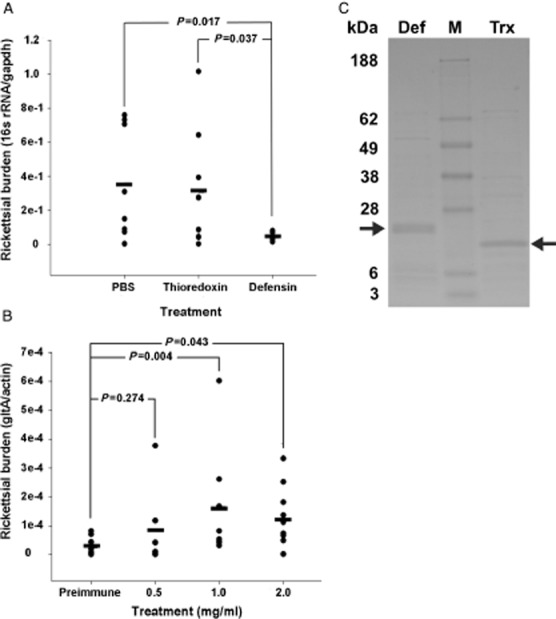
Defensin-2 limits Rickettsia montanensis infection in vitro and in vivo. (A) R. montanensis were incubated with recombinant defensin-2, phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or recombinant thioredoxin, and then used to infect an L929 monolayer for 24 h. Rickettsial burden in the infected L929 cells was determined using quantitative reverse transcriptase-PCR (qRT-PCR). The bar represents the average for each treatment. A total of four separate experiments were performed in duplicate (two wells per treatment). The number of samples analysed per treatment are as follows: untreated, n = 8; thioredoxin, n = 8; defensin-2, n = 7. (B) Part-fed Dermacentor variabilis ticks were capillary-fed anti-defensin-2 IgG at increasing concentrations followed by an oral R. montanensis challenge. Whole tissue was dissected and rickettsial burden determined using qRT-PCR. Each individual tick is represented by a closed circle. The mean for each treatment is represented by a bar. Values represent the transcript abundance measured in the total number of ticks collected from at least two separate experiments. P values were determined using the t-test. Biological replicates are as follows: preimmune, n = 10; 0.5 mg/ml, n = 8; 1 mg/ml, n = 8; 2 mg/ml, 10. (C) Representative Imperial blue stained lithium dodecyl sulfate (LDS) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of recombinant defensin-2 (Def) and thioredoxin (Trx) purification. Defensin-2 migrated to ∼28 kDa due to the thioredoxin and histidine fusion tags. M, molecular weight marker. Arrows indicate purified recombinant defensin-2 and thioredoxin.
