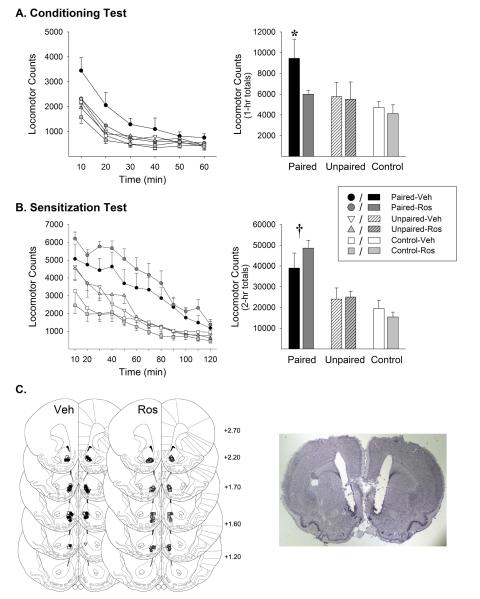
Figure 2.
NAcc roscovitine (Ros) administered during exposure blocked the induction of conditioned locomotion but spared the induction of locomotor sensitization. Time course (left) and session total locomotor counts (right) are shown for the 1-hour conditioning test (A) and 2-hour sensitization test (B). Data are shown as mean (±SEM). All rats were administered saline on the conditioning test and amphetamine (1.0 mg/kg, IP) on the sensitization test. Both tests were conducted 1 week following the exposure phase. Ros was not administered on either test. Group names refer to treatments administered during the exposure phase. *, p<0.05, compared to all other groups. †, p<0.05, either Paired-Veh or Paired-Ros compared to remaining groups. C. Line drawings (Paxinos and Watson, 1997) depicting location of microinjection cannula tips in the NAcc shell for rats included in the data analyses (left). Numbers indicate mm from bregma. The photomicrograph to the right shows a representative cresyl violet stained brain section with bilateral cannula tracks targeting the NAcc shell. n/group=5-7.