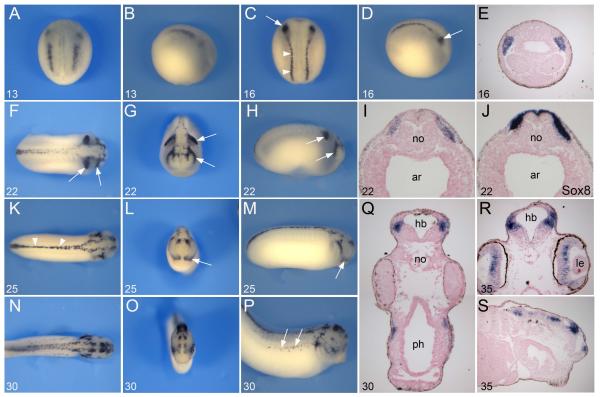
Figure 2. Developmental expression of Tfap2e by in situ hybridization.
(A-B) Tfap2e onset of expression at the NPB at stage 13. (C-D) At stage 16 Tfap2e expression extends to the entire length of the embryo, in region of the prospective trunk (arrowheads) and cranial NC. The most anterior segment of the cranial NC, the mandibular NC, shows stronger expression than the rest of the cranial NC (arrows). Panels (A, C), dorsal views, anterior to top. Panels (B, D), lateral views, anterior to right. (E) Transverse section of a stage 16 embryo, dorsal to top, showing Tfap2e expression in the mandibular NC. (F-H) At stage 22 as the neural tube closes, Tfap2e expression is restricted to the dorsal aspect of the spinal cord and in the most anterior and posterior segment of the migrating cranial NC (arrows). (I-J) On a transverse section of a stage 22 embryo Tfap2e and Sox8 have overlapping expression domains. (K-M) At stage 25 Tfap2e expression is detected in the mandibular NC (arrows), the dorsal aspect of the spinal cord (arrowheads) and in the brain. (N-P) At stage 30 Tfap2e expression is detected in the brain, dorsal neural tube and NC-derived melanocytes (arrows). (Q) Section of a stage 30 embryo at the level of the hindbrain. Transverse (R) and longitudinal (S) sections of a stage 35 embryo, showing expression in the brain and retina. Panels (F, K, N), dorsal views, anterior to right. Panels (G, L, O), frontal views, dorsal to top. Panels (H, M, P), lateral views, anterior to right. The stages are indicated in the lower left corner of each panel. ar, archenteron; hb, hindbrain; le, lens; no, notochord; ph, pharynx.