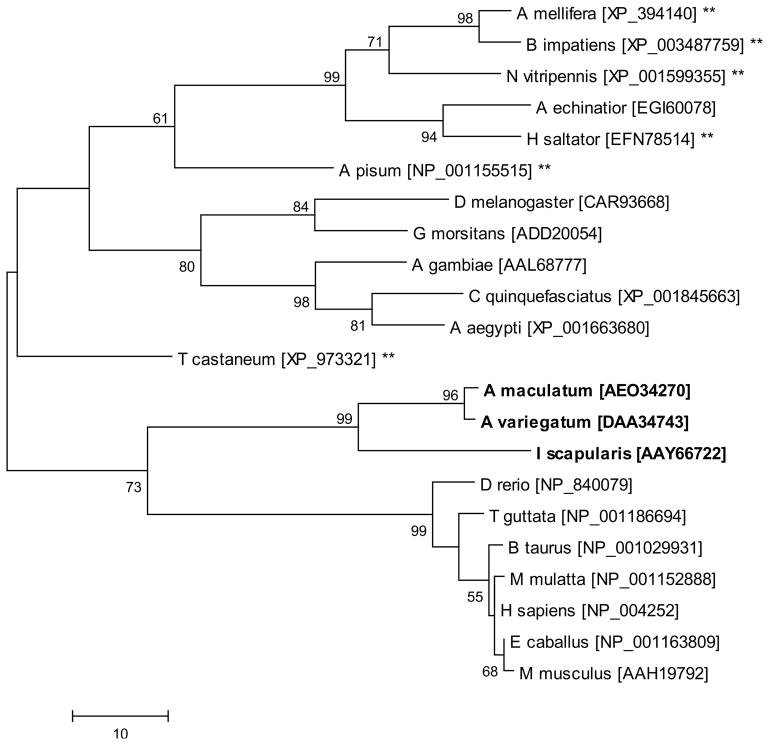
Figure 4.
The evolutionary history of Selenoprotein M was inferred using the Maximum Parsimony method. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) is shown next to the branches. Tick sequences are indicated in bold and sequences denoted with asterisks are derived from species which lack the capacity to synthesize selenoproteins and represent cysteine-containing homologs. Scale bar represents amino acid substitutions per position.