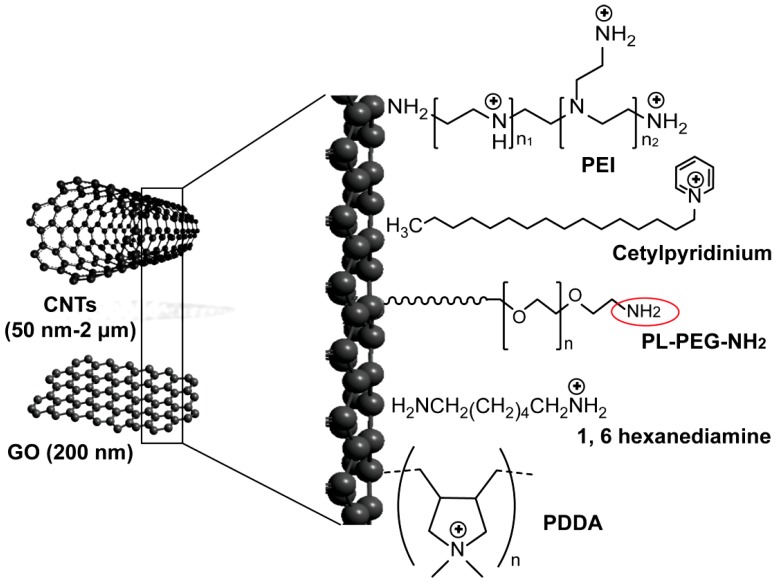
Figure 4.
Carbon-based nanoparticles for delivery of siRNA. Applied carbon nanostructures include multiwalled- and singlewalled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and single-atom-thick sheets of graphene oxide (GO). Ammonium-functionalized CNTs are prepared through non-covalent binding with cetylpyridinium chloride 209, tert-butyl-n-(6-aminohexyl)carbamate 92, and 1, 6 hexanediamine 95. Polymer coated-CNTs and GO are prepared through the addition of different positively charged polymers to their surfaces, including polyethylenimine (PEI) 106, 209 and poly(diallyldimethylammonium)chloride (PDDA) 94. Both ammonium-functionalized CNTs and polymer-coated CNSs are conjugated to siRNA by electrostatic interaction. CNTs can also be modified with non-covalent adsorption of phospholipid molecules carrying poly(ethylene glycol) (PL-PEG) chains with terminal amine or maleimide groups. This amine or maleimide terminal on the PL-PEG (red circle) permits the incorporation of thiolated siRNA by disulfide bond formation 91, 93.