Figure 3.
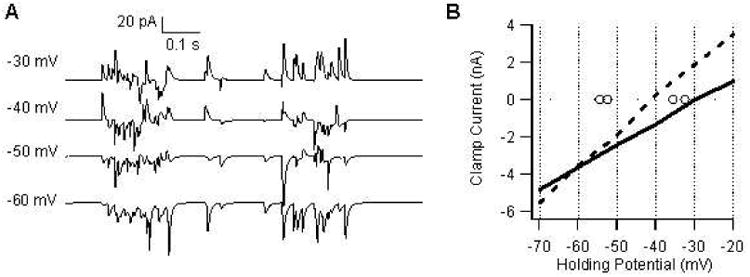
Reversal potential depends on distribution of synapses. (A) Simulated up-states in voltage clamp at potentials between −30 and −60 mV to demonstrate reversal of clamp current from inward to outward at a holding potential near −40 mV. The current is clearly inward at −60 mV, outward at −30 mV, and is a mixture of inward and outward at −40 mV. This pattern is similar to that observed experimentally (Blackwell et al., 2003). (B) Mean up-state current vs holding potential for equal distribution (solid line), or GABA redistributed toward soma (dashed line). The latter had a reversal potential of −43 mV, within the range of measured up-state reversal potentials (circles). Re-distributing the synaptic inputs lowers the reversal potential by approximately 12 mV.
