Figure 3. SIK2 phosphorylates CDK5R1/p35.
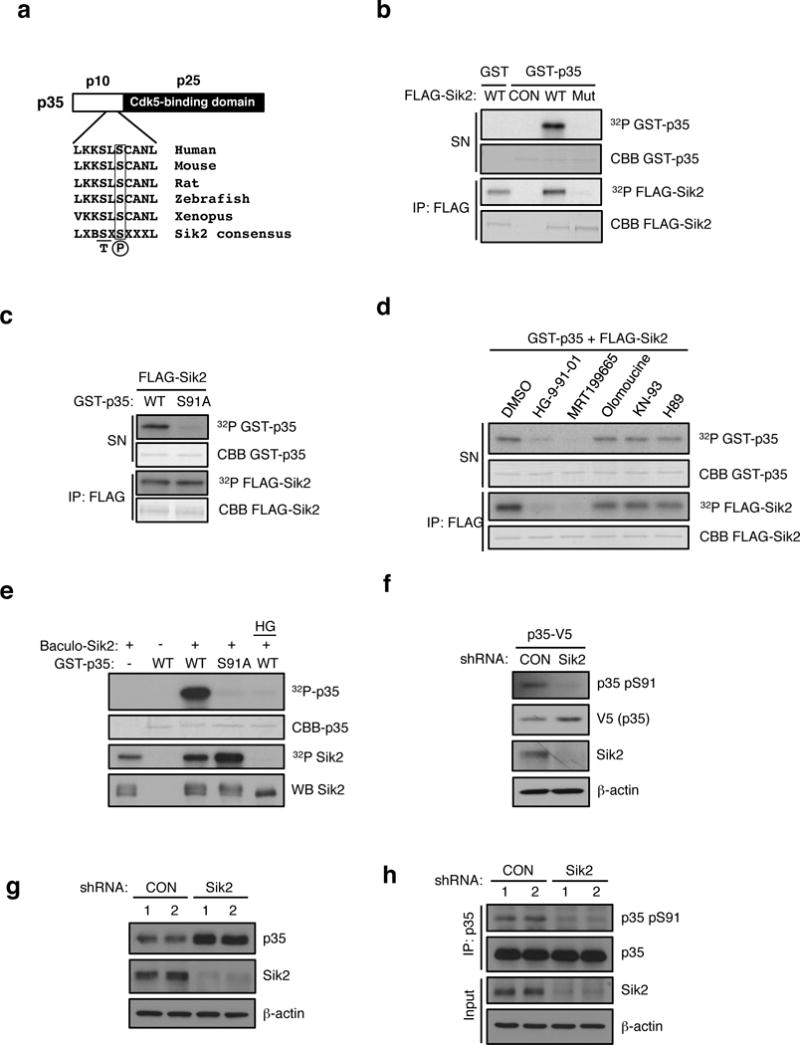
(a) Schematic of p35 showing N-terminal p10 domain, C-terminal p25 CDK5 binding domain and the location of Ser 91. Conservation of consensus SIK2 phosphorylation site at Ser91 of p35 using standard single letter amino acid nomenclature is shown. B= basic residue, X = any amino acid. (b) In vitro kinase assay using FLAG-SIK2 wild type (WT) or K49M kinase dead mutant (Mut) showing incorporation of 32P into full-length GST-p35 in the reaction supernatant. Autophosphorylation and coomassie blue staining of immunoprecipitated FLAG-SIK2 protein remaining on beads is shown in bottom two panels. CON = Empty vector control. (c) In vitro kinase assay using immunoprecipitates of FLAG-SIK2 and GST-p35 WT and S91A mutant as substrates. 32P and coomassie blue (CBB) staining of GST-p35 substrates and immunoprecipitated FLAG-SIK2 are shown. (d) In vitro kinase assay was performed with FLAG-SIK2 and GST-p35 WT in the presence of DMSO, HG-9-91-01 (100 nM), MRT199665 (200 nM), Olomoucine (60 μM), KN-93 (10 μM), or H89(1 μM). 32P and coomassie blue (CBB) staining of GST-p35 substrates and immunoprecipitated FLAG-SIK2 are shown. (e) In vitro kinase assay was performed with GST-p35 (WT and S91A) and recombinant SIK2 purified from Sf9 cells infected with baculovirus in the presence or absence of HG-9-91-01 (100 nM). (f) Western blot analysis of pSer91 levels on p35-V5 in MIN6 cells infected with non-targeting control (CON) or SIK2 shRNA with anti-p35 pSer91 antibody. (g) Western blot analysis of endogenous p35 levels in SIK2 knockdown MIN6 cells. (h) Western blot anaylsis of pSer91 levels in IPs of endogenous p35 in control or SIK2 shRNA expressing MIN6 cells treated with MG132 (10 uM for 24h). All western blot data are representative of three independent experiments with consistent results.
