Figure 6.
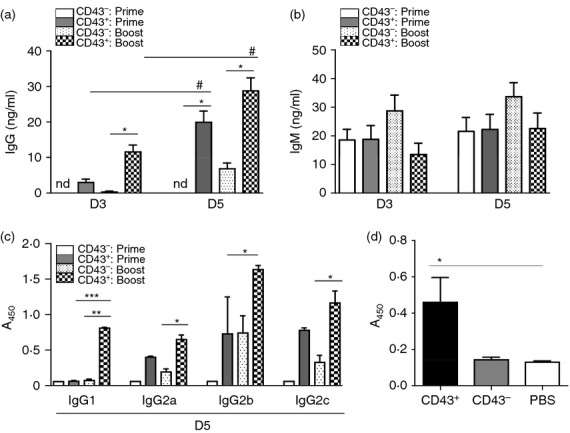
CD43+ B220− populations are major cell types contributing to in vitro antibody production. CD43+ or CD43− isolated cell fractions of splenocytes from ROSA yellow fluorescent protein transgenic mice (n = 3) by the MACS system were pooled and cultured for 3 (D3) or 5 (D5) days with A/PR8 virus-like particle (VLP) stimulator (1 μg/well). In vitro culture supernatants (100 μl) were used to measure the relative antibody concentrations for influenza virus (A/PR8) -specific IgG (a), IgM (b) and IgG isotype antibodies (c) determined by ELISA. CD43+: prime, CD43 positive splenocytes from 2 week prime immunized mice; CD43−: prime, CD43 negative splenocytes from 2 week prime immunized mice; CD43+: boost, CD43 positive splenocytes from 2 weeks boost immunized mice; CD43−: boost, CD43 negative splenocytes from 2 weeks boost immunized mice; nd, not detectable. This pattern of in vitro antibody production was consistent and the data shown were a representative out of three independent experiments. (d) IgG antibody responses in MHCII-deficient mice with adoptive transfer of CD43+ and CD43− fractionated populations from C57BL/6 mice followed by vaccination. Immunization of MHCII-deficient mice influenza VLP vaccine (A/PR8 VLP) was followed 4 hr after adoptive transfer. Serum antibody levels were determined at 2 weeks after immunization and presented as optical densities at 450 nm. (a–d) * or #, ** and ***; P < 0·05, 0·01 and 0·001, respectively. Horizontal statistical bars indicate comparing groups (*, **, *** comparison between CD43− versus CD43+ prime or boost; # comparison between D3 and D5).
