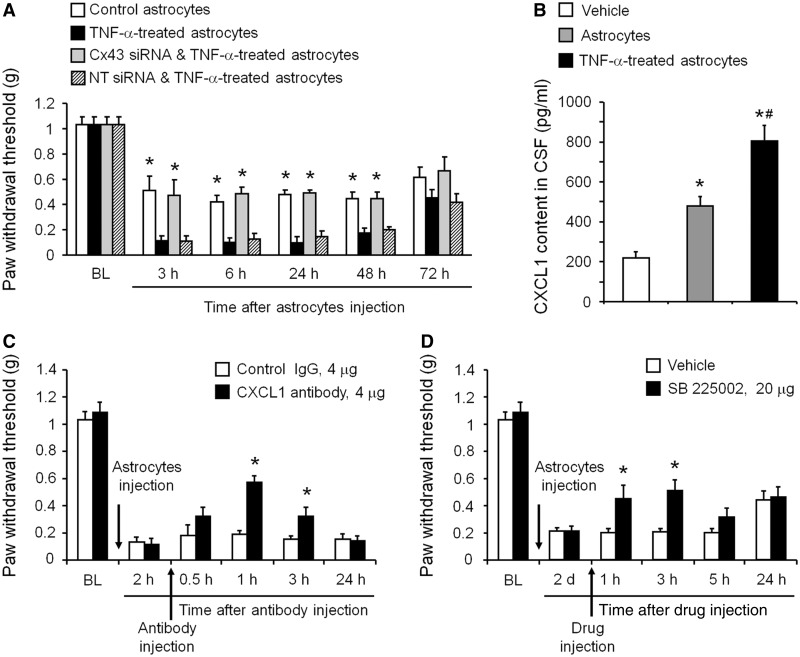
Figure 6.
Spinal injection of TNF-α-activated astrocytes induces mechanical allodynia via Cx43-mediated CXCL1 release. (A) Intrathecal injection of TNF-α-activated astrocytes elicited persistent mechanical allodynia for >48 h. Note this allodynia is reduced by pretreatment of astrocytes with Cx43 small interfering RNA (1 µg/ml, 18 h). *P < 0.05, compared with TNF-α or TNF-α + non-targeting control small interfering RNA treated group; n = 6 mice/group. (B) ELISA analysis shows increased CXCL1 release in the CSF at 3 h after the intrathecal injection of TNF-α-activated astrocytes. *P < 0.05, compared with vehcile group; #P < 0.05, compared with non-activated astrocytes; n = 4 mice/group. (C) Intrathecal injection of a CXCL1 neutralizing antibody (4 µg) transiently and partially reversed mechanical allodynia, induced by TNF-α-treated astrocytes. *P < 0.05, compared with control IgG group; n = 6 mice/group. (D) Intrathecal injection of the CXCR2 antagonist SB225002 (20 µg = 57 nmol) transiently and partially reversed mechanical allodynia, induced by TNF-α-activated astrocytes. *P < 0.05, compared with vehicle (PBS); n = 5–6 mice/group. All data are mean ± SEM. The differences between groups were analysed by ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls test.