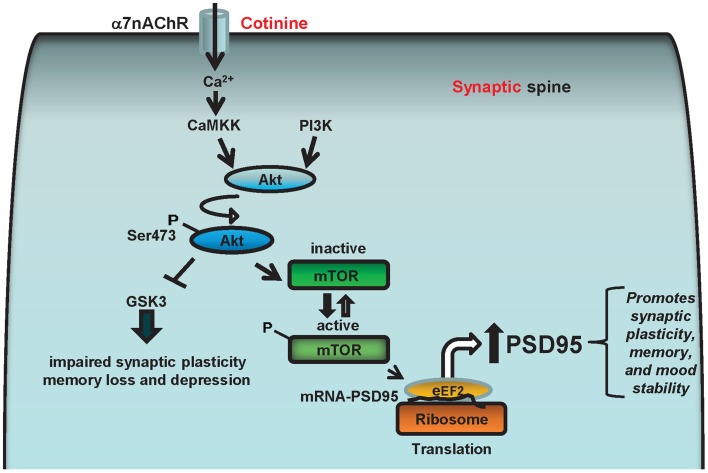
Figure 5.
Diagram representing the potential cell signaling pathways underlying the positive actions of cotinine on synaptic plasticity and behavior. The α7nAChRs can stimulate Akt (aka, protein kinase B) through the calcium-dependent activation of CaMKK, which can activate Akt that in turn phosphorylates and stimulates CREB and/or the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activity. The α7nAChR may also stimulate Akt through ERK/PI3K, and CREB and mTOR phosphorylation. mTOR, and CREB are serine threonine kinase, that regulate synaptic plasticity and memory formation. Also, mTOR positively controls the translational machinery to synthesize synaptic proteins such as PSD95 by stimulating the phosphorylation of the protein translation modulators eIF4E and 4EBP1. Therefore, cotinine may enhance the translation of PSD95 by activating ERK/PI3K/Akt and/or CamKK/Akt signaling pathways via positively modulating α7nAChR.