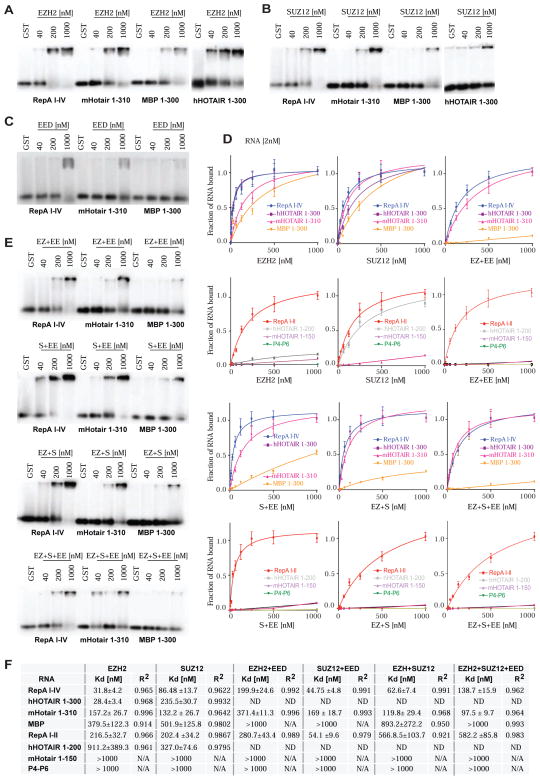
Figure 3. RNA binding potential of PRC2 subunits and subcomplexes.
(A) EMSA shows high affinity of EZH2 (concentrations shown) for RNA. (B) EMSA shows that SUZ12 also binds RNA but at higher concentrations. (C) EMSA shows that EED binds poorly to all tested RNAs. (D) Binding isotherms of PRC2 single subunits EZH2 and SUZ12, and subcomplexes: EZH2+EED (EZ+EE), SUZ12+EED (S+EE), EZH2+SUZ12 (EZ+S) and EZH2+SUZ12+EED (EZ+S+EE). Isotherms generated from data obtained from double-filter binding experiments. (E) EMSAs showing PRC2 subcomplexes interactions with long (≥300nt) RNAs. (First panel) shows that EED (EE) attenuates EZH2 (EZ) binding to RNA. (Second panel) EMSA shows that EED has modest effects on SUZ12 binding to RNA. (Third panel) EMSA shows that the EZH2-SUZ12 subcomplex (EZ+S) also binds RNA, but with lower affinity that EZH2 alone. (Bottom) EMSA of the EZH2-SUZ12-EED subcomplex (EZ+S+EE) showing reduced RNA binding. (F) Table of Kd and R2 values for PRC2 single subunits- and PRC2 subcomplexes-RNA interactions. Please also refer to Figure S2.