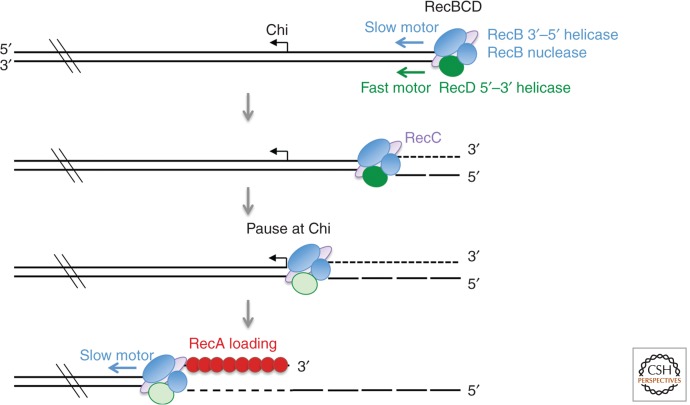
Figure 1.
End processing by the RecBCD complex. RecBCD loads at ends and translocates on both strands using the RecD and RecB helicase subunits. RecB degrades both DNA strands exiting the complex, but with more incisions on the 3′ strand than the 5′-terminated strand. RecBCD pauses at a Chi site, and the RecD subunit is modified; continued translocation is driven by the RecB helicase. After Chi recognition, RecB directs loading of RecA onto the 3′ end and degrades only the 5′ strand.