Figure 3. SIRT5 catalyzes lysine deglutarylation reactions in vitro and in vivo.
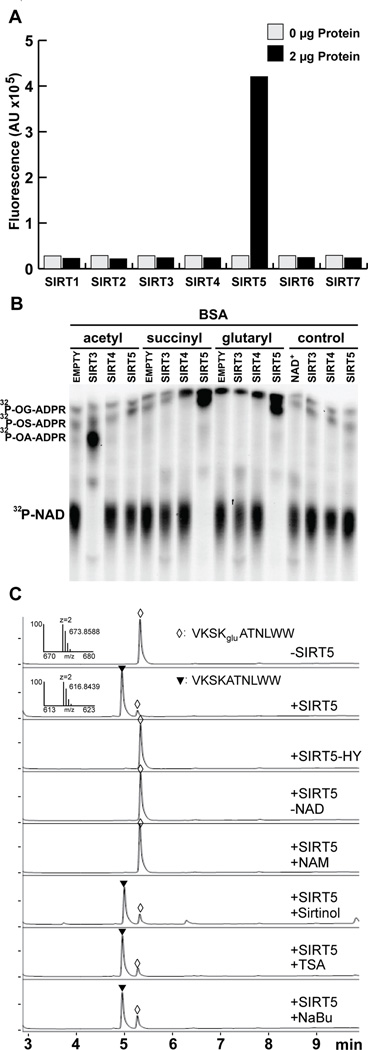
(A) Screening of HDAC lysine deglutarylation activity in vitro. Fluorometric assay to detect in vitro lysine deglutarylation activities using recombinant SIRT1-7.
(B) 32P-NAD+ consumption monitored by thin layer chromatography after an in vitro SIRT3, SIRT4, or SIRT5 enzymatic assay using chemically acylated BSA as a substrate; o-glutaryl-ADP ribose, OG-ADPR; o-succinyl-ADP ribose, OS-ADPR; o-acetyl-ADP ribose, OA-ADPR.
(C) HPLC trace of a glutarylated peptide, VKSKgluATNLWW, before and after in vitro deglutarylation reaction. The assays were carried out without hSIRT5, with hSIRT5, with enzymatically-inactive mutant of hSIRT5 (H158Y), without NAD+, with SIRT5 in the presence of nicotinamide (25 mM), or sirtinol (200 µM), or TSA (2 µM), or sodium butyrate (NaBu) (25mM). A triangle and a diamond indicate modified (HRMS, m/z, 673.8588 Da) and unmodified (HRMS, m/z, 616.8439 Da) peptides, respectively.
