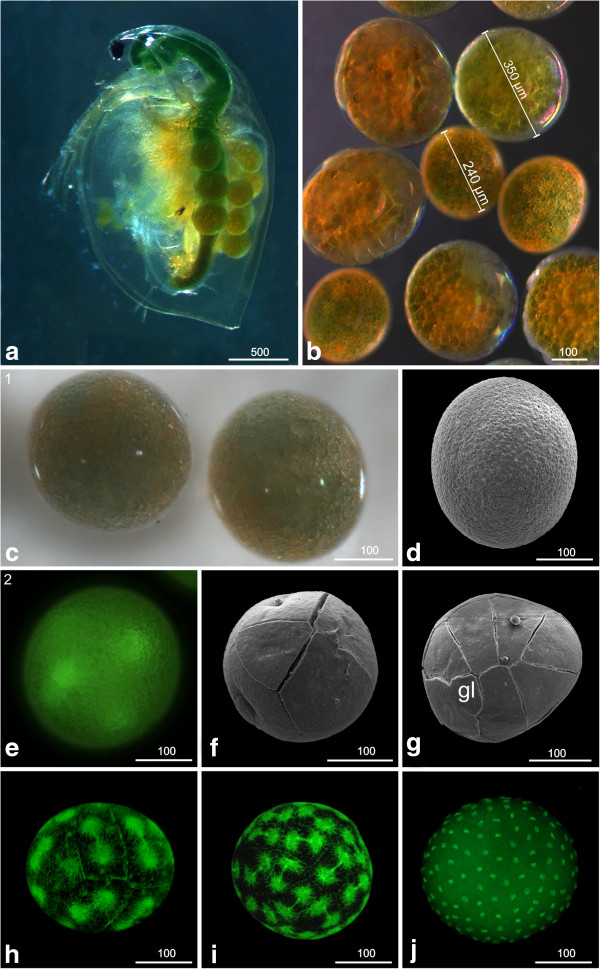
Figure 1.
Early developmental stages (stage 1: Egg cell (apomictic), (a-d); stage 2: Early cleavages, (e-j): a, b, c light microscopy; d, f, g SEM; e, h, i, j Sytox. (a) Female of D. magna carrying eggs in its brood pouch. The size of the eggs can vary even in one single female. (b) Eggs of several females. The size can vary by more than 60%. (c) Stage 1 (egg cell; apomictic); the nucleus lies within non-transparent globular pale to greenish yolk granules and a number of larger oil drops. (d) The egg is covered tightly by the chorion. (e) Stage 2 (Early cleavages); the first cleavages of the egg are intralecithal. (f) From the eight-nuclei stage onward, cell membranes are visible externally (arrowhead) and demarcate the blastomeres. (g) The 16-nuclei stage exhibits a characteristic arrangement of blastomeres which are unequal in size. One small cell indicated by a ‘gl’ could be the germ line precursor cell. (h) 16 to 32 cells. (i) 32 to 64 cells. (j) More than 512 cells. The first nine cleavage cycles are synchronous. gl = germ line.