Figure 4.
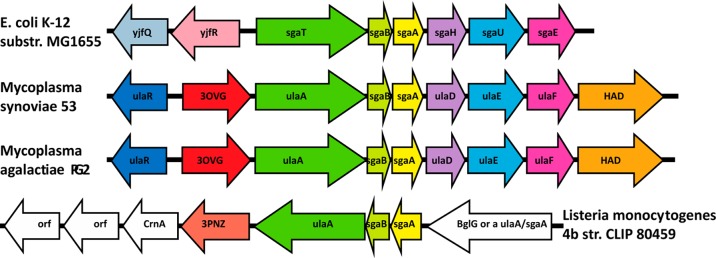
Gene organization of the operon and ulaA–G regulon involved in l-ascorbate metabolism in E. coli, which encodes a phosphotransferase system (PTS) (ulaABC genes). The putative functional analogues of the ula genes from M. synoviae 53, M. agalactiae PG2, and Listeria monocytogenes str. 4b are shown in the same colors. In red are the lactonases from M. synoviae 53, M. agalactiae PG2, and L. monocytogenes str. 4b. The gene names in order of M. synoviae 53 are ulaR/yjfq/rpiR transcriptional repressor for the l-ascorbate utilization ula divergon; Ms0025 hypothetical protein (phosphorylated sugar lactonase); ulaA/sgaT PTS system ascorbate-specific transporter subunit II, C component; sagB PTS system, IIB component, pentitol phosphotransferase enzyme II, B component; sgaA pentitol phosphotransferase enzyme II, A component; ulaD/sgaH 3-keto-l-gulonate-6-phosphate decarboxylase; ulaE/sgaUl-xylulose 5-phosphate 3-epimerase; ulaF/sagE/araDl-ribulose-5-phosphate 4-epimerase; MS53_0032, haloacid dehalogenase superfamily subclass Iib sugar phosphatase.
