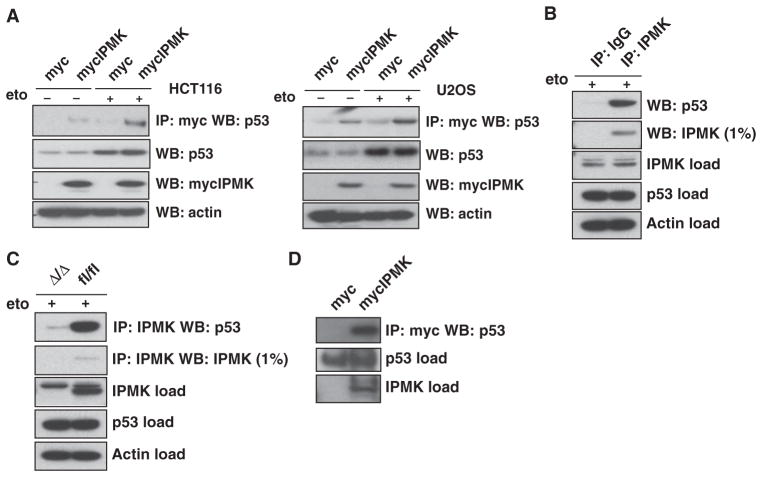
Fig. 1.
IPMK interacts with p53. (A) HCT116 cells (left panel) and U2OS cells (right panel) transfected with plasmid encoding myc-tagged IPMK (mycIPMK) and treated overnight with 20 μM etoposide (eto) were lysed and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-myc agarose. IPMK and p53 were resolved from the immunoprecipitated samples by SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and identified by Western blotting (WB). Inputs for p53, mycIPMK, and actin are shown in the bottom blots. (B) Wild-type primary MEFs treated with 20 μM etoposide were lysed and subjected to immunoprecipitation with normal immunoglobulin G (IgG) or antibody specific for IPMK. SDS-PAGE and Western blotting were performed as described in (A). (C) Lysates from IPMK-deficient (Δ/Δ) and floxed wild-type (fl/fl) MEFs were used as described in (B) to assess endogenous IPMK-p53 binding. (D) Immunoprecipitation of purified mycIPMK and bacterially purified p53, as assessed by immunoprecipitation with anti-myc agarose and subsequent protein resolution and identification by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. Blots in all panels are representative of at least three experiments.