Figure 1.
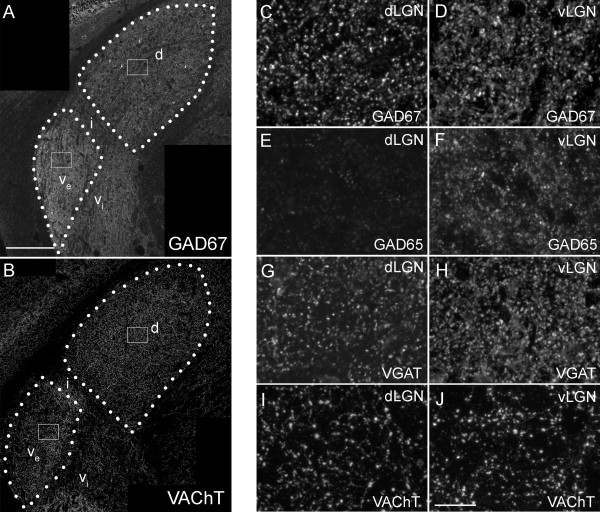
Distribution of inhibitory and modulatory nerve terminals in subnuclei of mouse visual thalamus. A,B. Confocal images of immunohistochemistry (IHC) for GAD67 (A) and VAChT (B) in coronal sections of adult mouse LGN. Outlines of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (dLGN) and the external division of the ventral lateral geniculate nucleus (vLGN) are depicted with white dots. d, dLGN; ve, external division of vLGN; vi, internal division of vLGN; i, IGL. White boxes depict regions enlarged in C,D,I, and J. C,D. High magnification images of GAD67-immunoreactivity in dLGN (C) and vLGN (D) from the regions boxed in A. E,F. High magnification images of GAD65-immunoreactivity in dLGN (E) and vLGN (F). Note the lack of GAD65-immunoreactivity in dLGN. G,H. High magnification images of VGAT-immunoreactivity in dLGN (G) and vLGN (H). High magnification images of VAChT-immunoreactivity in dLGN (I) and vLGN (J) from the regions boxed in B. All images are maximum projection confocal images. Scale bar in A = 200 μm for A,B and in J = 25 μm for C-J.
