Fig. 3. rHIgM22, a recombinant human IgM, promotes remyelination of spinal cord demyelination.
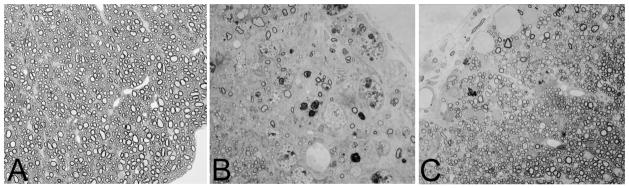
Light photomicrographs of normal spinal cord white matter showing densely packed myelinated axons (A). A typical demyelinated lesion with minimal remyelination as observed in the spinal cord of a susceptible mouse infected with Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus for 5 months. This mouse was treated five weeks earlier with a control human IgM that does not bind to the surface of oligodendrocytes. The area contains only a few remyelinated axons. Infiltrating macrophages in the demyelinating lesion are characterized by the presence of darkly stained debris-laden vesicles (B). In contrast, much remyelination is observed in areas of chronic spinal cord demyelination of mice treated with rHIgM22, a recombinant human IgM that binds to myelin and the surface of oligodendrocytes (C). An area of nearly complete remyelination is present in the ventral lateral spinal cord after a single 50 μg dose intraperitoneally of rHIgM22 five weeks earlier. Remyelination is characterized by densely packed thin myelin sheaths in relation to axon diameter. Panels A, B and C are the same magnification.
