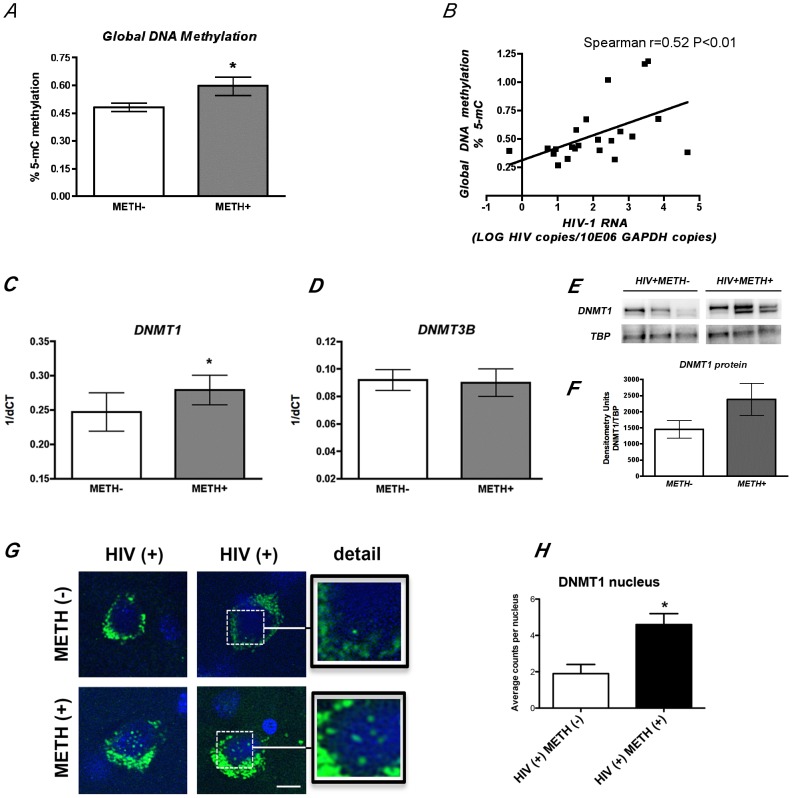
Figure 2. METH use results in increased global DNA methylation in the brains of HIV seropositive cases.
A. Global methylation was determined by ELISA quantification of 5-mC on genomic DNA from frontal cortex samples. Significant increase in DNA methylation was observed in HIV seropositive METH users. *p<0.05 by Wilcoxon matched pairs test. B. Cellular HIV-1 RNA levels correlate with DNA methylation levels as determined by Spearman correlation between global DNA methylation and log HIV-1 RNA in the brain R = 0.527 with p = 0.01. C. Quantitative real-time PCR showed significant increase in DNMT1 transcript levels on HIV seropositive individuals who used METH. D. METH exposure did not alter mRNA levels of DNMT3B, a closely related family member reported to have redundant functions to DNMT1 in the brain. *p<0.05 by Wilcoxon matched pairs test. E. Western blot analysis of DNMT1 protein content in the nucleus showing representative HIV+METH− and HIV+METH+ cases. F. Image analysis showing integrated pixel intensity of Dnmt1 immunoreactivity. G. Immunofluorescence detection of DNMT1 on frontal cortex sections. Green fluorescent signal correspond to DNMT1 immunoreactivity and blue signal corresponds to DAPI nuclear staining. H. Image analysis showing average DNMT1 positive nuclear counts. Bar represents 10 µm. One way ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance, *p<0.05.