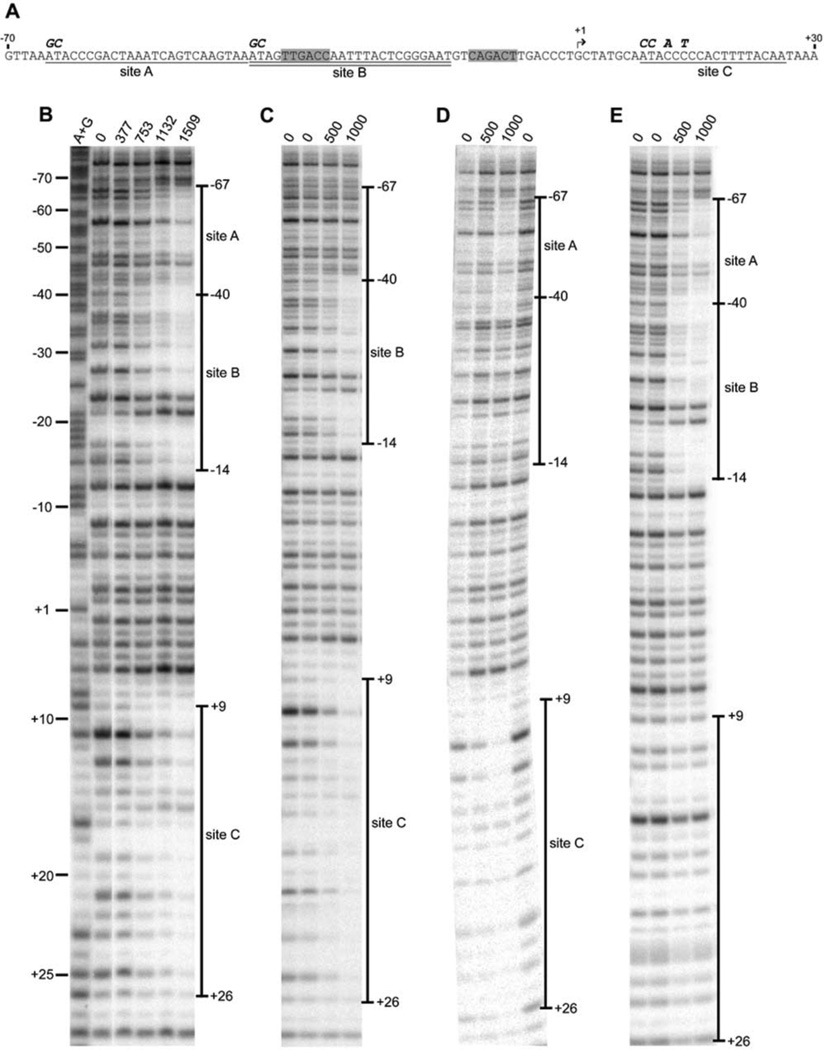
Fig. 1.
In vitro binding of anaerobically purified [2Fe-2S]-IscR to wild-type and mutated IscR binding sites within PiscR. A) The IscR binding sites A (underlined), B (double underlined), C (underlined), the transcriptional start site (bent arrow), the −35 and −10 promoter elements (shaded),and the bases substituted in this study (bold italics) are indicated. DNase I footprints of IscR bound to DNA fragments containing the wild-type PiscR region (panel B) or promoter regions with mutations in sites A, B, or C (panels C, D, and E, respectively). The amount of IscR protein (nM) present in each reaction and the extent of the footprint relative to the +1 transcription start site are denoted. Samples were electrophoresed with Maxam-Gilbert (A + G) ladders. The lane order in panel B was digitally rearranged for presentation purposes.