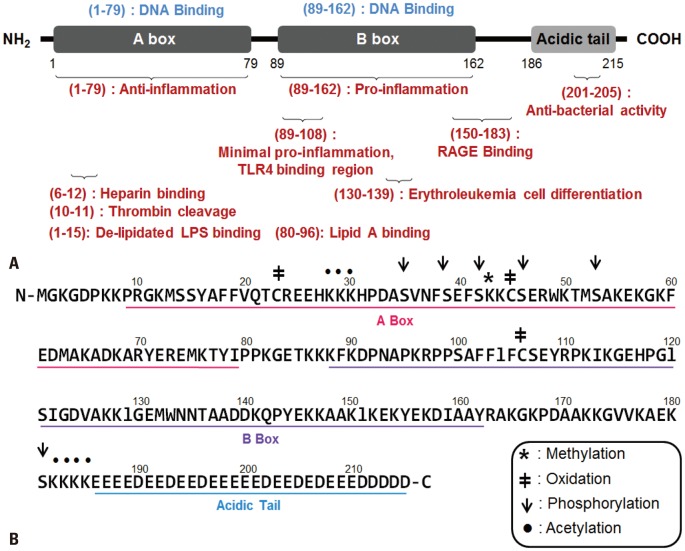
Fig. 1.
Structure of HMGB1. (A) HMGB1 protein is composed of 215 amino acids in three structural domains: the A box (1-79), B box (89-162), and the acidic C tail (186-215). The A box functions in DNA binding and inducing anti-inflammatory effects, whereas the B box domain plays an important role in DNA binding and stimulating proinflammatory responses. The B box domain consists of two crucial binding sites for TLR4 and RAGE that mediate the release of proinflammatory cytokines. In particular, the 20 amino acids of the TLR4 binding site (89-108) are the minimal sequence needed to induce cytokine activity. Two peptide regions (3-15, 80-96) of HMGB1 bind to delipidated LPS and lipid A regions, respectively. (B) The functional component of HMGB1 is represented in a linear diagram underlining the amino acid residues that constitute the A box domain (pink), B box domain (purple), and C tail (blue). Symbols are used to denote specific sites for the four post-translational modifications that HMGB1 goes through during active secretion: methylation, oxidation, phosphorylation, and acetylation.